Case 12 Winding and twisting
Introduction
In this course, students will learn how to program XGO Rider to perform complex Z-shaped forward motion. This not only involves a deep understanding of robot motion control, but also requires students to master the relevant knowledge of path planning. Through the study of this course, students will be able to improve their comprehensive application capabilities in robot programming and control.
Teaching objectives
Understand the kinematic principles of Z-shaped forward motion.
Learn how to implement XGO Rider's Z-shaped path planning through programming.
Improve students' problem-solving ability and innovative thinking.
Teaching preparation
Before starting teaching, please make sure you have prepared the following necessary materials:
 | micro:bit V2 |
|---|---|
 | XGO-Rider |
 | USB Cable |
 | PC |
These materials will provide you with a complete experience and ensure that you can smoothly carry out subsequent operations and learning. If you are ready for the above, we can proceed to the next step.
 After turning on the XGO Rider, in order to keep the fuselage balanced, it needs to move back and forth slightly. Please do not place the XGO Rider on the edge of the table or in a dangerous place to avoid damage.
After turning on the XGO Rider, in order to keep the fuselage balanced, it needs to move back and forth slightly. Please do not place the XGO Rider on the edge of the table or in a dangerous place to avoid damage. Teaching process
Course introduction
Z-shaped forward movement is a common robot path planning action, which requires the robot to flexibly change direction during the forward movement to adapt to different environments and task requirements. In this course, we will guide students to learn how to program the XGO Rider to perform a Z-shaped forward movement, which will help students better understand the robot's motion control and path planning.
Exploration Activities
- What is the kinematic principle of the robot when it moves in a zigzag pattern?
- How to implement the zigzag path planning of XGO Rider through programming?
Start programming
Add XGO Rider software library
1. Go to "makecode.microbit.org" and click New Project.

2.Enter a project name in the pop-up window and click Create.

3. Click Extension in the code drawer, enter XGO Rider in the search box on the pop-up interface and click the search icon. Click it after the XGO Rider software library is displayed.

Sample Program

Reference program link: https://makecode.microbit.org/_3gw411CxqEz0
 Because XGO Rider's performance mode has forward and backward movement, please place XGO Rider on a spacious flat ground.
Because XGO Rider's performance mode has forward and backward movement, please place XGO Rider on a spacious flat ground.
Download the program
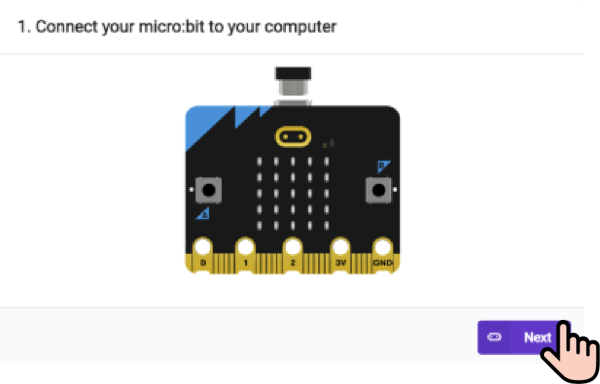
1. Use a USB cable to connect PC and micro:bit V2.

2. After the connection is successful, a drive letter named MICROBIT will be recognized on the computer.

3. Click  in the lower left corner and select Connect Device.
in the lower left corner and select Connect Device.

4. Click 。
。
5. Click 。
。
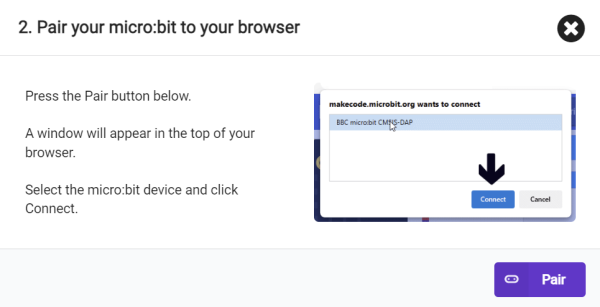
6. Select BBC micro:bit CMSIS-DAP in the pop-up window, and then select Connect. At this point, our micro:bit has been successfully connected.

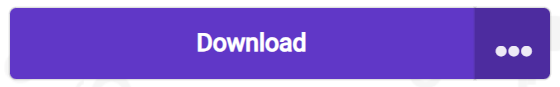
7. Click Download program.
Teamwork and Presentation
Students are divided into groups to jointly complete the programming of XGO Rider's Z-shaped forward movement.
Students are encouraged to cooperate, communicate and share experiences with each other.
Each group has the opportunity to show their programmed XGO Rider to other groups and demonstrate.
Expected results:
Summary and reflection
Review the course content and remind students what knowledge and skills they have mastered?
Guide students to discuss the problems and difficulties they encountered during the production process and how to solve these problems.
Guide students to think and discuss together how to optimize the Z-shaped forward movement of XGO Rider.
Extended knowledge
The kinematic principle of the Z-shaped forward movement involves the robot's steering mechanism and path planning algorithm. In practical applications, this usually requires the robot to be able to perceive the surrounding environment and adjust its motion trajectory in real time. Sensors, such as ultrasonic sensors, infrared sensors or cameras, can provide the necessary environmental information to help the robot avoid obstacles and plan the best path.
When programming to achieve zigzag movement, a variety of algorithms can be used, such as the A* search algorithm, the Dijkstra algorithm, or the behavior-based path planning method. These algorithms can calculate an optimal or feasible path based on the robot's current position, target position, and environmental information.
In addition, zigzag movement can also be achieved by controlling the speed difference between the left and right wheels of the robot. This method requires precise control of the speed and direction of the motor to ensure that the robot can perform zigzag movements smoothly.
Through the study of this course, students can not only master the programming skills of zigzag movement, but also have a deep understanding of the basic principles of robot motion control and path planning, laying a solid foundation for more complex robot applications in the future.