Case 03 Your Name
Introduction
In this course, we will show students how to set the Bluetooth name of XGO Rider and obtain its firmware version number through programming. Students will first understand the basic principles of Bluetooth technology, and then learn in depth how to modify the name of a Bluetooth device through programming. In addition, the course will explain the basic concepts and importance of firmware, and guide students to master the relevant programming skills for obtaining the firmware version number. Through these studies, students will be able to interact with XGO Rider more proficiently and improve their programming practice.
Teaching Objectives
- Understand the principles of Bluetooth technology.
- Learn to modify the Bluetooth name of XGO Rider through programming.
- Understand the role of firmware in smart devices.
- Learn to obtain the version number of XGO Rider firmware through programming.
Teaching Preparation
Before starting teaching, please make sure you have prepared the following necessary materials:
 | micro:bit V2 |
|---|---|
 | XGO-Rider |
 | USB Cable |
 | PC |
These materials will provide you with a complete experience and ensure that you can smoothly carry out subsequent operations and learning. If you are ready for the above content, we can proceed to the next step.
 After turning on the XGO Rider, in order to keep the fuselage balanced, it needs to move back and forth slightly. Please do not place the XGO Rider on the edge of the table or in a dangerous place to avoid damage.
After turning on the XGO Rider, in order to keep the fuselage balanced, it needs to move back and forth slightly. Please do not place the XGO Rider on the edge of the table or in a dangerous place to avoid damage.
Teaching process
Course introduction
In the previous course, we have mastered how to communicate and interact with the XGO Rider through programming. However, just as we usually ask the other person's name when we meet for the first time, it is equally important to know its "name" when interacting with the XGO Rider. In this class, we will guide you to learn how to set the Bluetooth name for the XGO Rider and obtain the firmware version number through programming, that is, to give it a unique identifier. You can even give it a meaningful name according to your preferences. So, let's start the learning journey of this section.
Exploration Activities
Why are the three primary colors red, green and blue? Are other colors possible?
How is sound produced? What is the range of sound that humans can hear?
How to control the rainbow lights and speakers of XGO Rider through programming?
Start Programming
Add XGO Rider Software Library
1. Go to "makecode.microbit.org" and click New Project.

2. Enter the project name in the pop-up window and click Create.

3. Click Extension in the code drawer, enter XGO Rider in the search box on the pop-up interface and click the search icon. Click it after the XGO Rider software library is displayed.

Sample Program

Reference Program Link: https://makecode.microbit.org/_0gT2Evd1cTqv
 Because XGO Rider has forward and backward movement in the performance mode, please place XGO Rider on a spacious flat ground.
Because XGO Rider has forward and backward movement in the performance mode, please place XGO Rider on a spacious flat ground.
Download Program
1. Use a USB cable to connect PC and micro:bit V2.

2. After the connection is successful, a drive letter named MICROBIT will be recognized on the computer.

3. Click  in the lower left corner and select Connect Device.
in the lower left corner and select Connect Device.

4. Click 。
。
5. Click 。
。
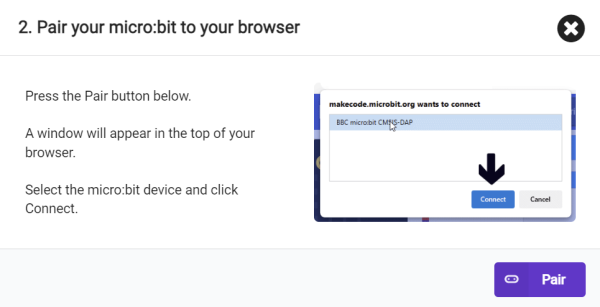
6. Select BBC micro:bit CMSIS-DAP in the pop-up window, and then select Connect. Now our micro:bit has been successfully connected.

7. Click Download Program.
Teamwork and Presentation
Students are divided into groups to complete the programming of setting the Bluetooth name of XGO Rider and obtaining the firmware version number.
Encourage students to cooperate, communicate and share experiences with each other.
Each group has the opportunity to show their programmed XGO Rider to other groups and demonstrate.
Expected results:

Summary and reflection
Review the course content and remind students what knowledge and skills they have mastered?
Guide students to discuss the problems and difficulties they encountered during the production process and how to solve these problems.
Guide students to think and discuss whether they can set the Bluetooth name of XGO Rider arbitrarily.
Expand knowledge
Bluetooth technology
Bluetooth technology is a wireless communication standard mainly used for data and voice transmission over short distances. It allows electronic devices to communicate through wireless signals without physical connection. The core principles of Bluetooth technology include the following aspects:
Radio frequency: Bluetooth uses the 2.4 GHz ISM (Industrial, Scientific, Medical) band for communication, which is an unlicensed band and is also a common band for many wireless technologies.
Frequency hopping technology: In order to reduce interference and improve signal stability, Bluetooth uses frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) technology. This means that Bluetooth devices will constantly change the operating frequency when transmitting data, thereby avoiding staying on one frequency for a long time.
Data transmission: Bluetooth devices transmit data via radio waves, which are encoded into digital signals. The Bluetooth protocol defines the structure and transmission method of data packets to ensure that data is reliably transmitted between devices.
Device pairing: Two Bluetooth devices need to be paired before the first communication. This process involves security authentication between devices to ensure that only authorized devices can connect.
Low power design: Bluetooth technology is particularly suitable for battery-powered devices because it is designed with multiple power saving modes to reduce power consumption when no data is transmitted.
Multi-device connection: Bluetooth technology supports connections between multiple devices. A device can communicate with multiple devices at the same time, which is very useful in some application scenarios, such as audio devices can connect to multiple audio sources at the same time.
Protocol stack: Bluetooth technology has a complete set of protocol stacks, including the physical layer, link layer, logical link control and adaptation protocol layer (L2CAP), service discovery protocol (SDP), etc. These protocols define how devices establish connections, transmit data and discover services.
After years of development, Bluetooth technology has launched multiple versions, such as Bluetooth 4.0, Bluetooth 4.2, Bluetooth 5.0, etc. Each new version has improved in terms of increasing transmission rate, reducing power consumption and adding functions.
Smart device firmware
The firmware of smart devices is software embedded in hardware devices. It plays a vital role. Its main functions include:
Control hardware operation: The firmware interacts directly with the hardware to control the device's startup process, configure hardware parameters, and manage the basic functions of the device.
Provide a user interface: Firmware can contain an operating system or applications that provide an operating interface for users to interact with the device.
Ensure device security: Firmware often contains security protocols and encryption mechanisms to help protect devices from malware and hacker attacks.
Updates and maintenance: Through firmware updates, manufacturers can fix security vulnerabilities, improve performance, add new features, or improve device compatibility.
Diagnostics and troubleshooting: Firmware can contain diagnostic tools to help identify and solve hardware or software problems.
Optimize performance: Firmware can adjust the performance of the device to ensure that hardware resources are used most efficiently.
Support network communication: Firmware handles the device's network connection, including wireless communication protocols such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, ensuring that the device can communicate with other devices or the Internet.
Implement specific functions: In some devices, firmware is also responsible for implementing specific functions, such as automation control in smart home devices.
In short, firmware is the cornerstone of the normal operation of smart devices. It defines how the device operates and ensures that the device can perform its designed tasks safely and efficiently.