Case 06: Light Control
Introduction
This course aims to introduce students to the working principle of the car headlights. Students will use TPbot Edu to learn how to write programs to control the lights of the car.
Teaching Objectives
Learn to use Makecode software to create programs to control the lights of the car.
Teaching Preparation
Before starting the teaching, please make sure you have prepared the following necessary materials:
| Picture | Name | Number | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
 | TPbot Edu | 1 | |
 | USB Cable | 1 | |
 | micro:bit | 1 | Prepare Yourself |
 | PC | 1 | Prepare Yourself |
Course Introduction
Are you ready to enter the wonderful world of colored lights? In this lesson, we will learn how to control the color of lights and make them change colors like a rainbow. We will first understand how the color of light is obtained and how to control color electronically.
Exploration Activities
How to control the color of lights?
Software
Programming
Click Advanced in the code drawer of MakeCode to see more code options.

In order to program TPbot Edu, we need to add an extension library. Find Extensions at the bottom of the code drawer and click it. A dialog box will pop up, search for tpbot, and then click to download this code library.
Sample Program
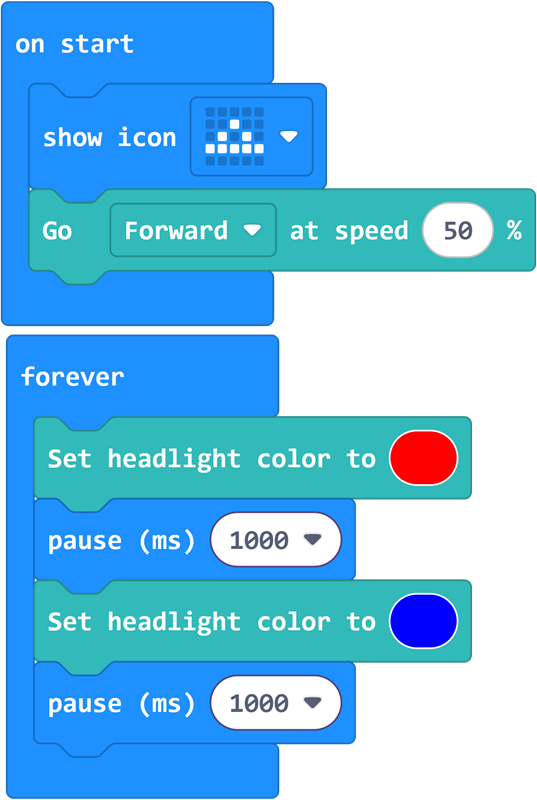
Program
Please refer to the program link: https://makecode.microbit.org/_FsuAE7eoqKd5
You can also download the program directly from the following website.
Conclusion
When powered on, the car moves forward, and the headlights alternate between red and blue lights.
Extended Knowledge
Primary colors of light and additive color principle
Primary colors of light and additive color principle are fundamental concepts in color science that explain how light is used to create various colors. Here is a brief introduction to these concepts:
Primary colors of light The three primary colors of light are red, green, and blue (RGB). These three colors of light can be mixed in different proportions to produce all other colors. In the mixing of light, all the light is added up, so this principle is called the additive color principle.
Additive color principle The additive color principle refers to the process of creating new colors by adding different colors of light. When you mix two or more primary colors of light, they add together to produce a brighter color. Here are some key points about the additive color principle:
Primary color mixing:
Red + Green = Yellow Green + Blue = Cyan Blue + Red = Magenta
Full color light:
When red, green, and blue light are all mixed at their highest intensity, they produce white light.
Complementary colors:
Each color has a complementary color, and when complementary colors are mixed in the proper proportions, they produce white light. Complementary colors include: Red and Cyan Green and Magenta Blue and Yellow
Color saturation and brightness:
By adjusting the intensity of each primary color light, colors of varying brightness and saturation can be produced. Increasing the intensity makes the color brighter, and decreasing the intensity makes the color darker or closer to black.
Color space:
The RGB color model is widely used in electronic display devices such as televisions, computers, and mobile phone screens, which display millions of colors by adjusting the intensity of the three RGB primary colors.
Understanding the three primary colors of light and the additive color principle is essential for any work involving light and color, whether in art, design, photography, or video production. Through these principles, we can create rich and colorful visual experiences.