Case 05: Obstacle Avoidance
Introduction
This course aims to introduce students to the principles of obstacle avoidance and the working principle of ultrasonic sensors. Students will use TPbot Edu to learn how to write programs to control the car's obstacle avoidance.
Teaching Objectives
Understand the working principle of ultrasonic sensors
Learn to use Makecode software to create programs to control the car's obstacle avoidance.
Teaching Preparation
Before starting teaching, make sure you have prepared the following necessary materials:
| Picture | Name | Number | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
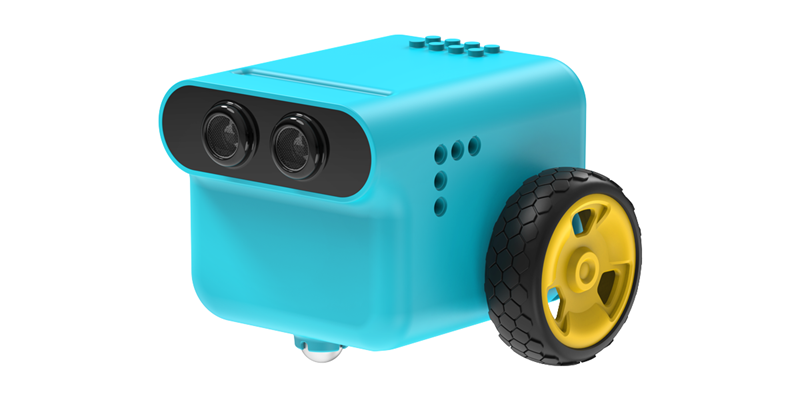 | TPbot Edu | 1 | |
 | USB Cable | 1 | |
 | micro:bit | 1 | Prepare Yourself |
 | PC | 1 | Prepare Yourself |
Course Introduction
Welcome to a new chapter in our smart car programming course - obstacle avoidance. In previous courses, we learned how to control the driving distance and steering angle of the smart car, and how to make the car follow a predetermined path. Today, we will explore how to make the smart car, like a real driver, able to identify and avoid obstacles and reach the destination safely.
The Importance of Obstacle Avoidance Obstacle avoidance is a basic function in autonomous driving technology, which involves multiple aspects such as environmental perception, decision making, and vehicle control. Through this technology, smart cars can stand out in complex environments and ensure driving safety and efficiency.
How Ultrasonic Sensors Work We will first understand how ultrasonic sensors work. Ultrasonic sensors measure the distance to obstacles by emitting ultrasonic waves and receiving their echoes. This principle is simple but powerful, and it provides our smart car with the ability to "see" obstacles.
How the car achieves obstacle avoidance Next, we will explore how the car uses these sensor data to achieve obstacle avoidance. When the sensor detects an obstacle in front, the car needs to make a decision whether to stop, go around it, or take other actions. We will learn how to control the behavior of the car through programming so that it can automatically avoid obstacles.
Exploration Activities
How does the ultrasonic sensor work?
How to make the car avoid obstacles?
Software
Programming
Click Advanced in the code drawer of MakeCode to view more code options.

In order to program TPbot Edu, we need to add an extension library. Find Extensions at the bottom of the code drawer and click it. A dialog box will pop up, search for tpbot, and then click to download this code library.
Sample Program
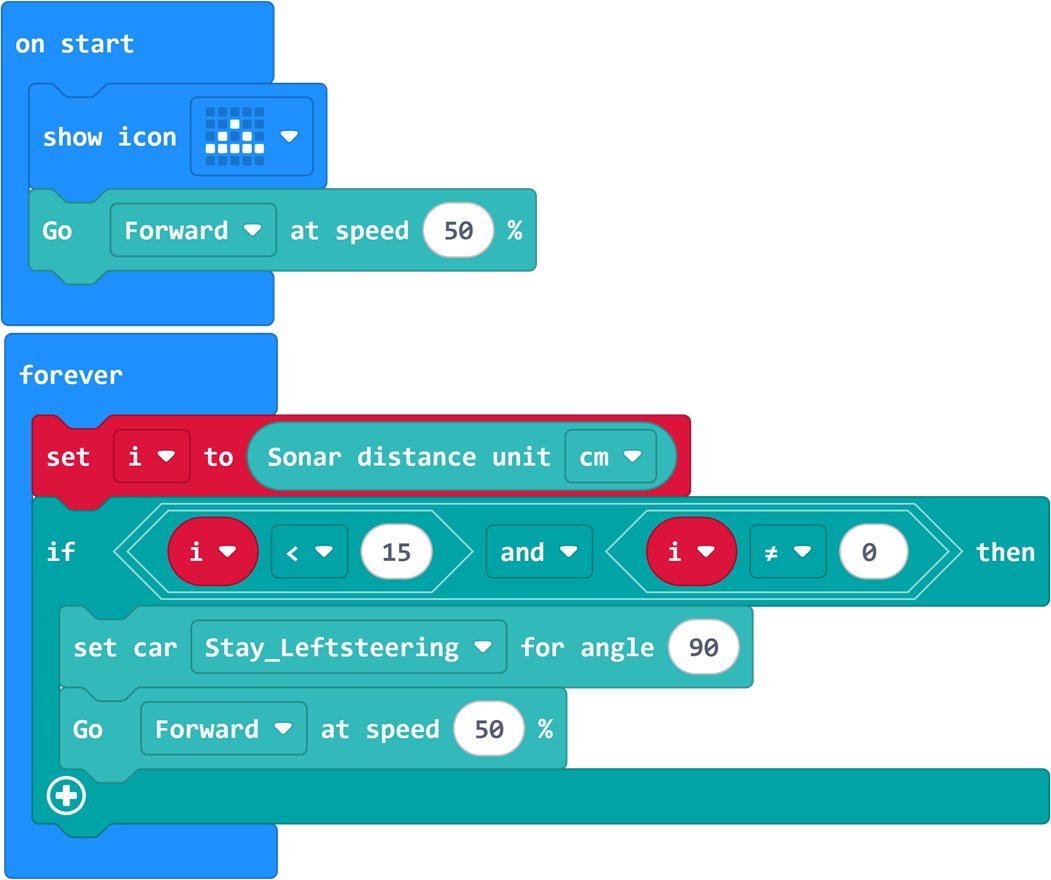
Program
Please refer to the program link: https://makecode.microbit.org/_J31Lxs86LTw6
You can also download the program directly from the following website.
Conclusion
When powered on, the cart moves forward and automatically turns 90 degrees if it encounters an obstacle.
Extended Knowledge
The working principle of ultrasonic sensors*
The working principle of an ultrasonic sensor is based on the emission and reception of sound waves, which can be used to measure distance, speed or to detect the presence of an object. Below is a concise description of how ultrasonic sensors work:
Emitting sound waves
Emitter Ultrasonic sensors have a transmitter that emits high frequency sound waves (ultrasound) that are inaudible to the human ear.
Receiving Reflection
Reflection of sound waves When the emitted sound waves meet an obstacle, they reflect back like an echo.
Receiver There is also a receiver on the sensor to receive these reflected back sound waves.
**Calculation of distance
**Time measurement The sensor calculates distance by measuring the time it takes for a sound wave to be sent out and received back. Since the speed of propagation of sound waves is known, the distance between the sensor and the obstacle can be calculated from the time.
Application Scenarios
Ultrasonic sensors are used in a wide variety of applications, such as sensing of automatic doors, obstacle avoidance systems for robots, and reversing radar for automobiles.
Through this simple but effective way, ultrasonic sensors can help devices and machines “sense” the surrounding environment, realize automatic control and intelligent interaction.