Case 03: Precision Steering
Introduction
This course aims to introduce students to the concepts of graphical programming and gyroscopes. Students will use TPbot Edu to learn how to write programs to control the steering angle of the car.
Teaching Objectives
Understand the basic concepts of gyroscopes.
Learn to use Makecode software to create programs to control the steering angle of the car.
Teaching Preparation
Before starting teaching, make sure you have prepared the following necessary materials:
| Picture | Name | Number | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
 | TPbot Edu | 1 | |
 | USB Cable | 1 | |
 | micro:bit | 1 | Prepare Yourself |
 | PC | 1 | Prepare Yourself |
Course Introduction
After successfully exploring how to control the driving distance of TPbot Edu through graphical programs in the last class, today we will enter a more exciting topic: controlling the steering angle of the car. Have you ever wondered how to make a car turn and avoid obstacles flexibly like a real car?
In this class, we will unveil the mystery of the gyroscope and learn how to use it to accurately control the steering angle of TPbot Edu. The gyroscope is a sensor that can sense and measure the angle of rotation. It plays a vital role in our smart car.
Now, let's start this exciting learning journey and explore how to make TPbot Edu turn freely in various environments!
Exploration Activities
How to use the graphical programming module to control the direction of the car's rotation?
The basic principles of the gyroscope and how it helps us measure angles.
Software
Programming
Click Advanced in the code drawer of MakeCode to see more code options.

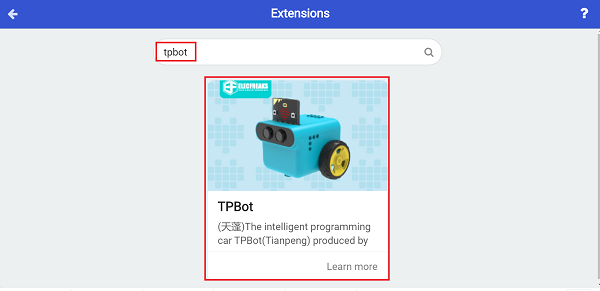
In order to program TPbot Edu, we need to add an extension library. Find Extensions at the bottom of the code drawer and click it. A dialog box will pop up, search for tpbot, and then click to download this code library.
Sample program
Drag a block called "Move forward 0 cm" and a block called "Set the car to turn left 0 degrees" from the block drawer and put them into "When button A is pressed", and modify the parameters as shown below.
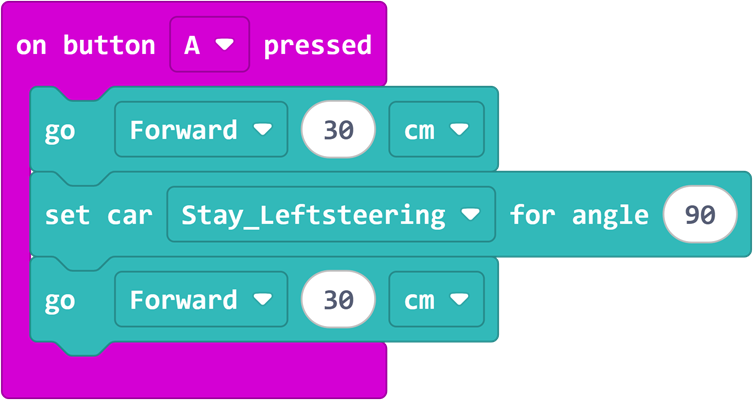
Program
Please refer to the program link: https://makecode.microbit.org/_1giUsjcL93Uy
You can also download the program directly from the following website.
Conclusion
When button A is pressed, TPbot Edu first moves forward 30cm, then turns left 90° on the spot, and finally moves forward 30cm.
Extended knowledge
A gyroscope is a device that can measure and maintain direction. Its principle is based on the conservation of angular momentum. Below I will explain the working principle of a gyroscope in simple and easy-to-understand language:
Basic concept of gyroscope
Imagine that you have a spinning gyroscope. When you put it on the ground, it will keep the same direction of rotation, even if the ground is tilted. This is the basic property of a gyroscope: it can resist changes in direction.
How gyroscope works
High-speed rotating wheel: There is a very small but high-speed rotating wheel inside the gyroscope, which we call a rotor. This rotor is like a gyroscope. Once it starts to rotate, it will maintain the direction of rotation.
Angular momentum: The high-speed rotation of the rotor produces a property called angular momentum. Angular momentum is a physical quantity that describes the "amount" of rotation of an object. The greater the angular momentum, the stronger the ability of the object to resist changes in direction.
Influence of external forces: When the housing (frame) of the gyroscope rotates, the rotor resists this rotation and maintains its original direction due to the conservation of angular momentum. This resistance causes the rotor axis to shift relative to the housing.
Measuring the shift: Gyroscopes have sensors inside that can detect the shift of the rotor axis. These sensors can be photoelectric sensors or accelerometers, which can convert mechanical shifts into electrical signals.
Signal processing: These electrical signals are then amplified, filtered and converted, and finally become digital signals that tell us the shift of the rotor axis relative to the initial position, that is, the angle of rotation.
Applications of gyroscopes
This feature of gyroscopes makes them useful in many fields, such as:
Navigation systems: In the navigation systems of aircraft, ships and cars, gyroscopes can help determine direction and attitude.
Mobile phones and game controllers: In smartphones and game controllers, gyroscopes can detect the tilt and rotation of the device, providing a more natural interactive experience.
Robotics: In robotics, gyroscopes can help robots maintain balance, or keep the correct orientation when moving.
Through these principles, gyroscopes can accurately measure and maintain orientation, providing important support for our technology and devices.