Case 11 Speech Recognition Cart
Introduction
The purpose of this lesson is to guide students to use the Nezha Inventor's Kit V2 and the AI Accessories Pack to create an intelligent cart that can control the driving route through voice commands. Through this project, students will learn how to combine voice recognition technology with robot control, develop their STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Math) skills, and improve problem-solving and creativity.

Teaching Objectives
- Understand the basic principles and applications of speech recognition technology.
- Learn about the evolution of speech recognition technology.
- Learn to build an intelligent cart with speech recognition capabilities.
- Improve teamwork and creative problem solving skills.
Teaching Preparation
ELECFREAKS NEZHA Inventor's Kit V2
Computer
Teaching Process
Introduction
Teachers can guide students to think about the following questions: the prospects for the application of speech recognition technology.
Hello everyone, today we're going to enter the world of technology and learn how to make an exciting voice-recognized cart using the Nezha Inventor's Kit V2 and AI Accessories Pack. Have you ever wanted to control the route of your cart with just your voice? That's the question we're going to tackle together today, so let's get started on this creative and technically challenging project.
Exploration
Break out into groups and have students think about how they can use an AI camera to create a voice-recognition cart.
- What is speech recognition technology and how does it apply to intelligent trolley control systems?
- How to design and implement voice commands to control the trolley's driving route?
Exploration
Work in groups to create a voice-recognition cart from building block materials according to your own design.
Follow your own design plan and use the building block materials to create a voice recognition cart.
Illustration
Building Step

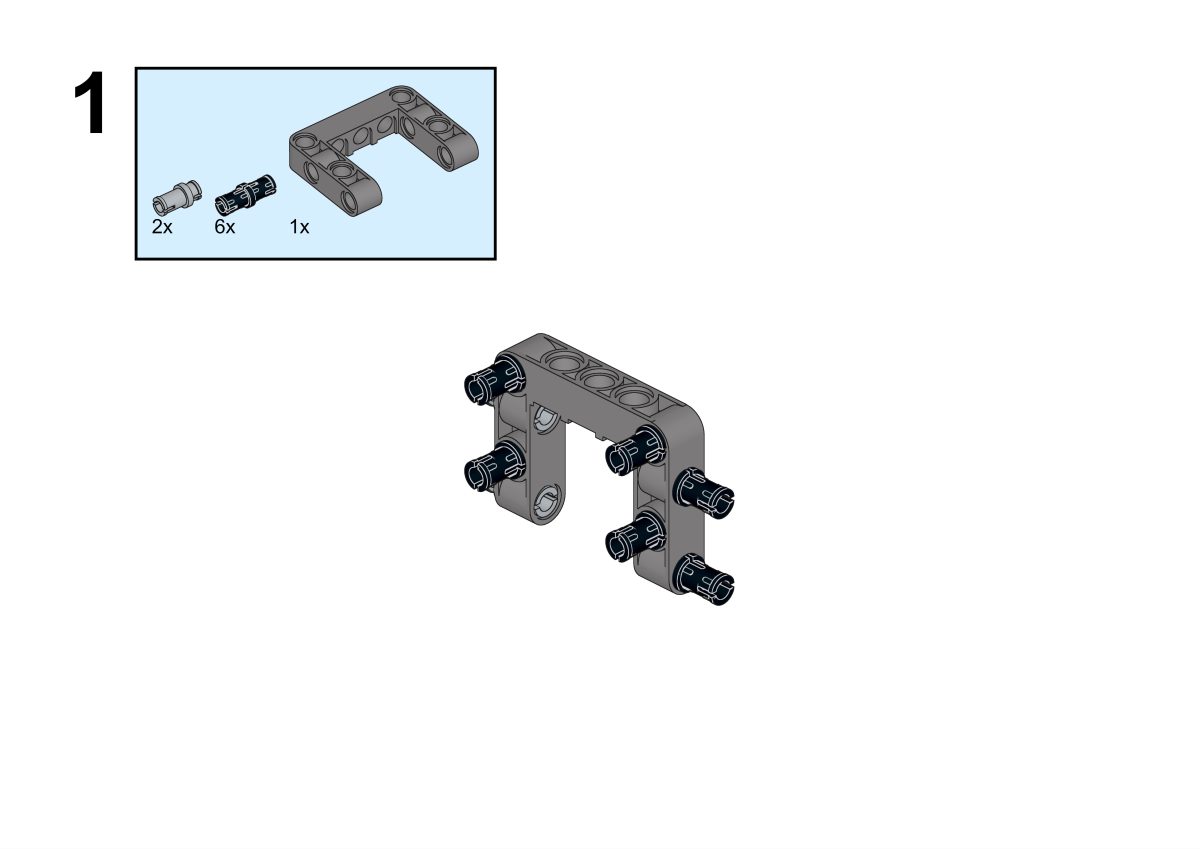




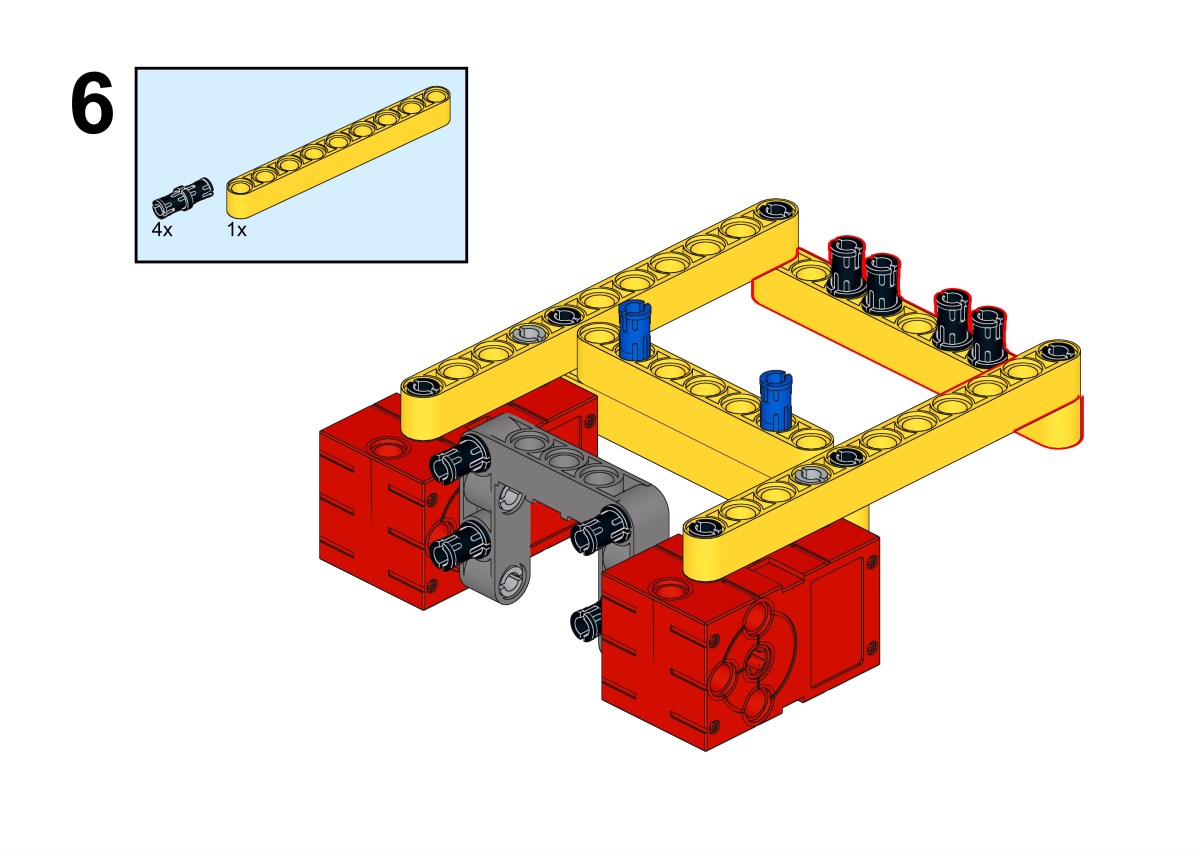
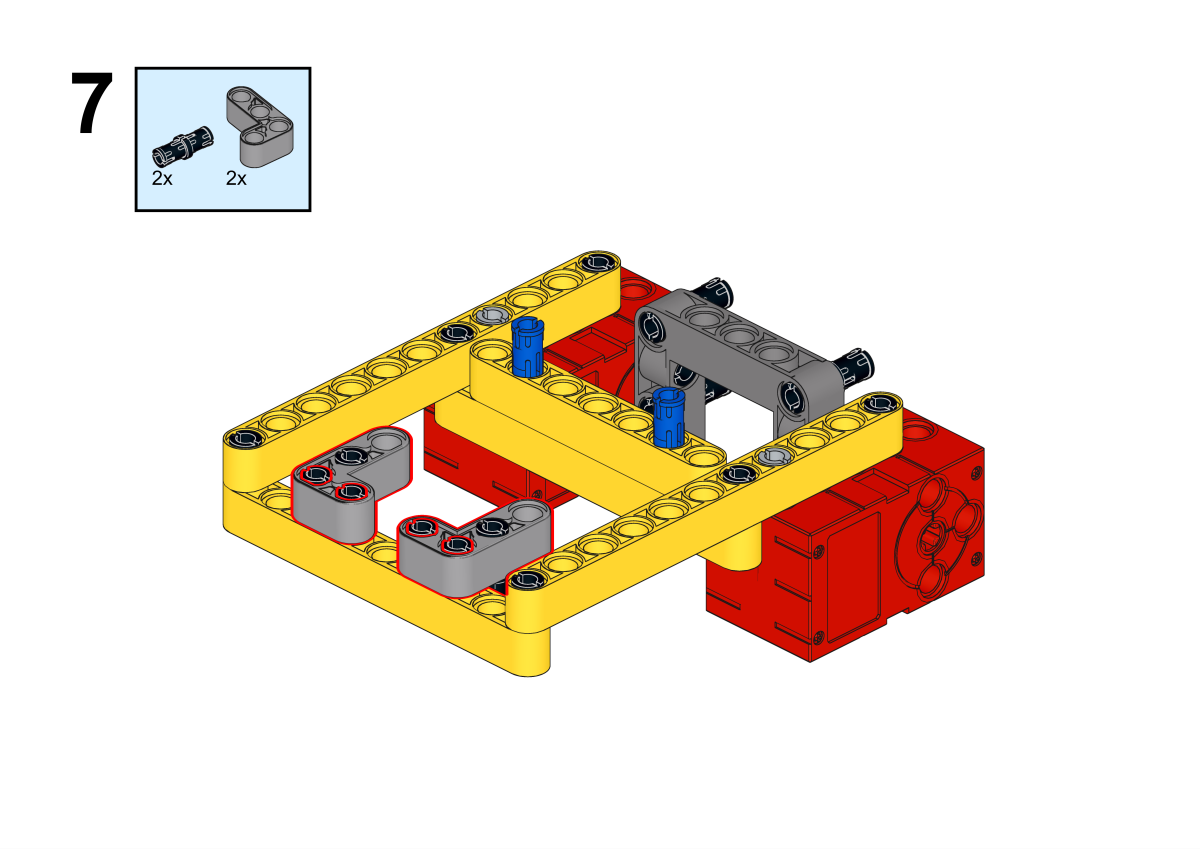
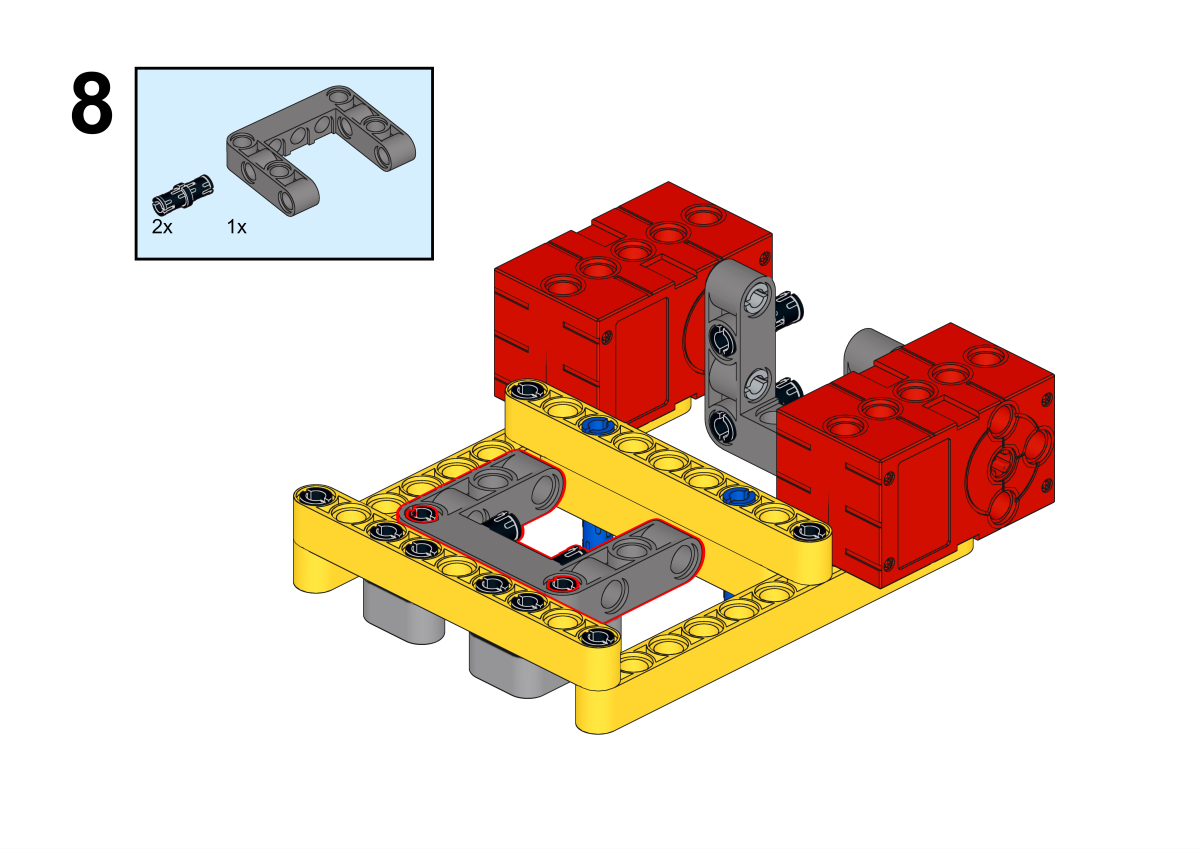





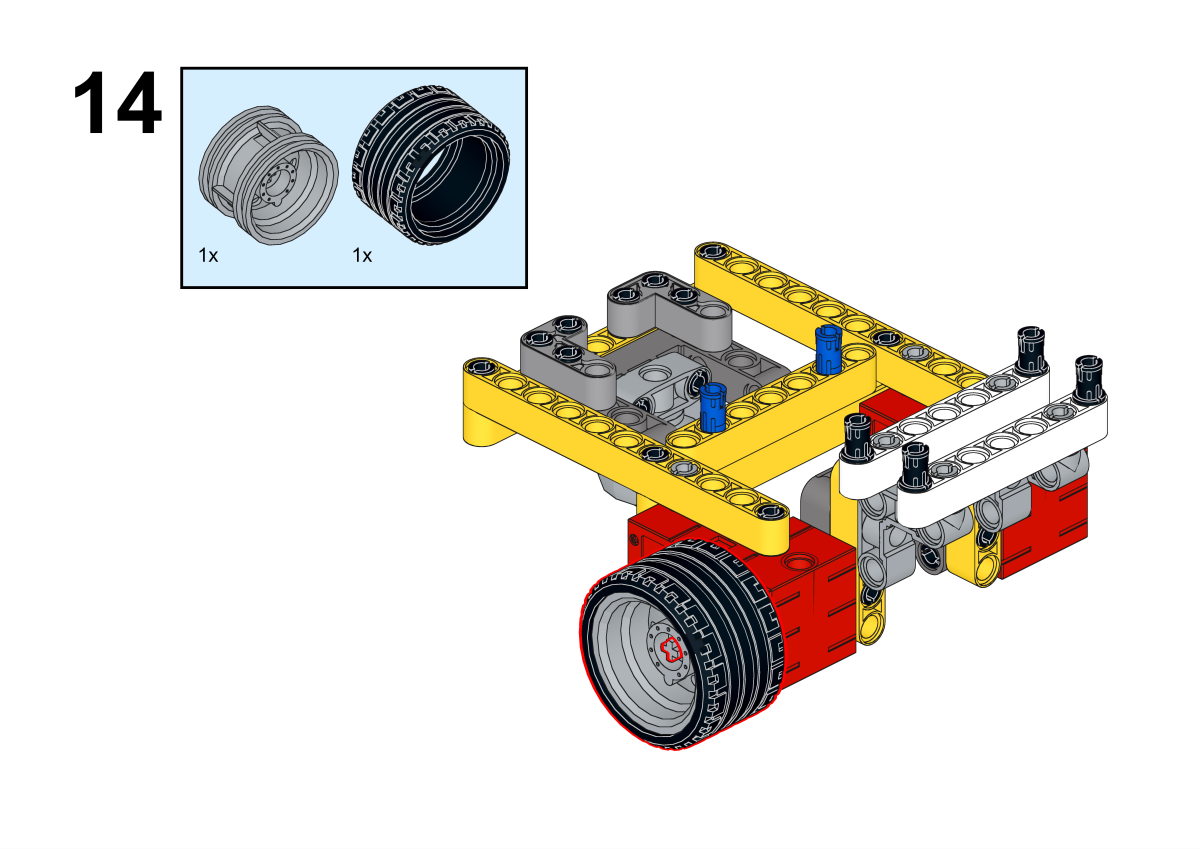
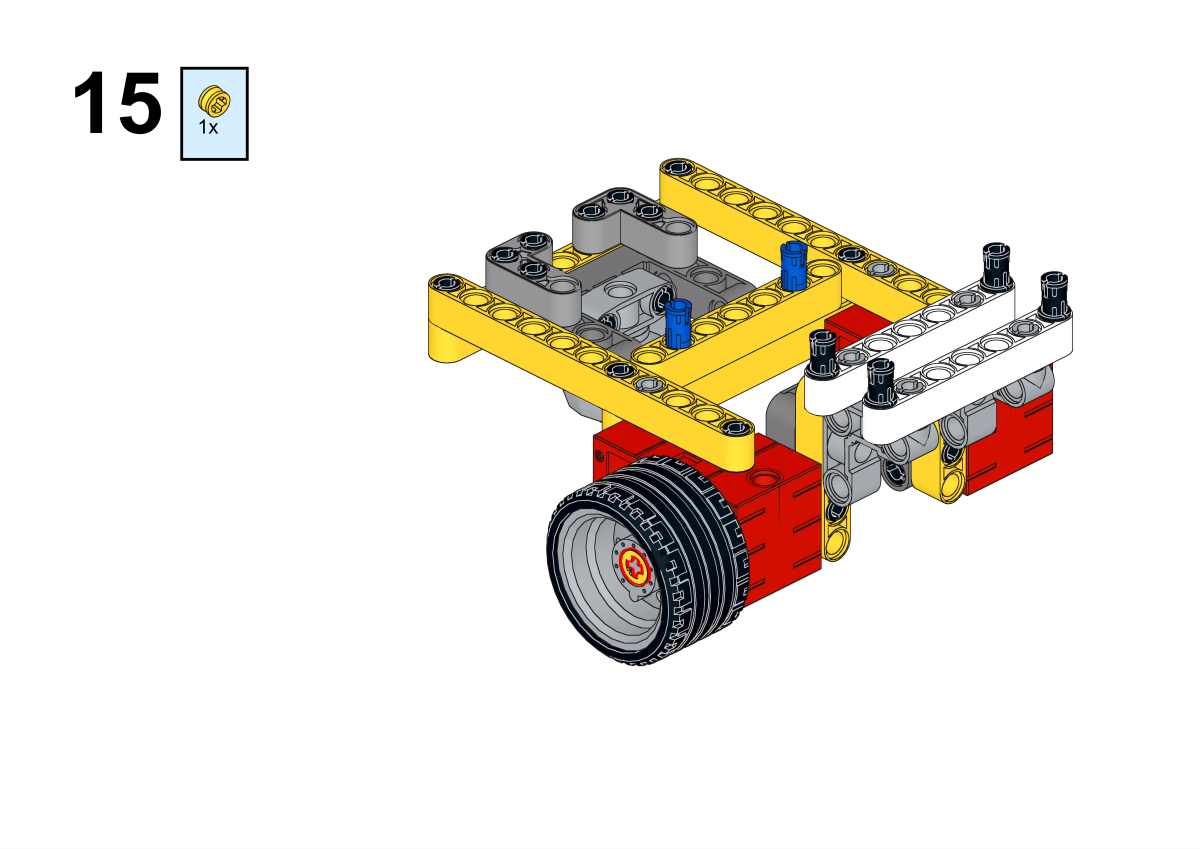
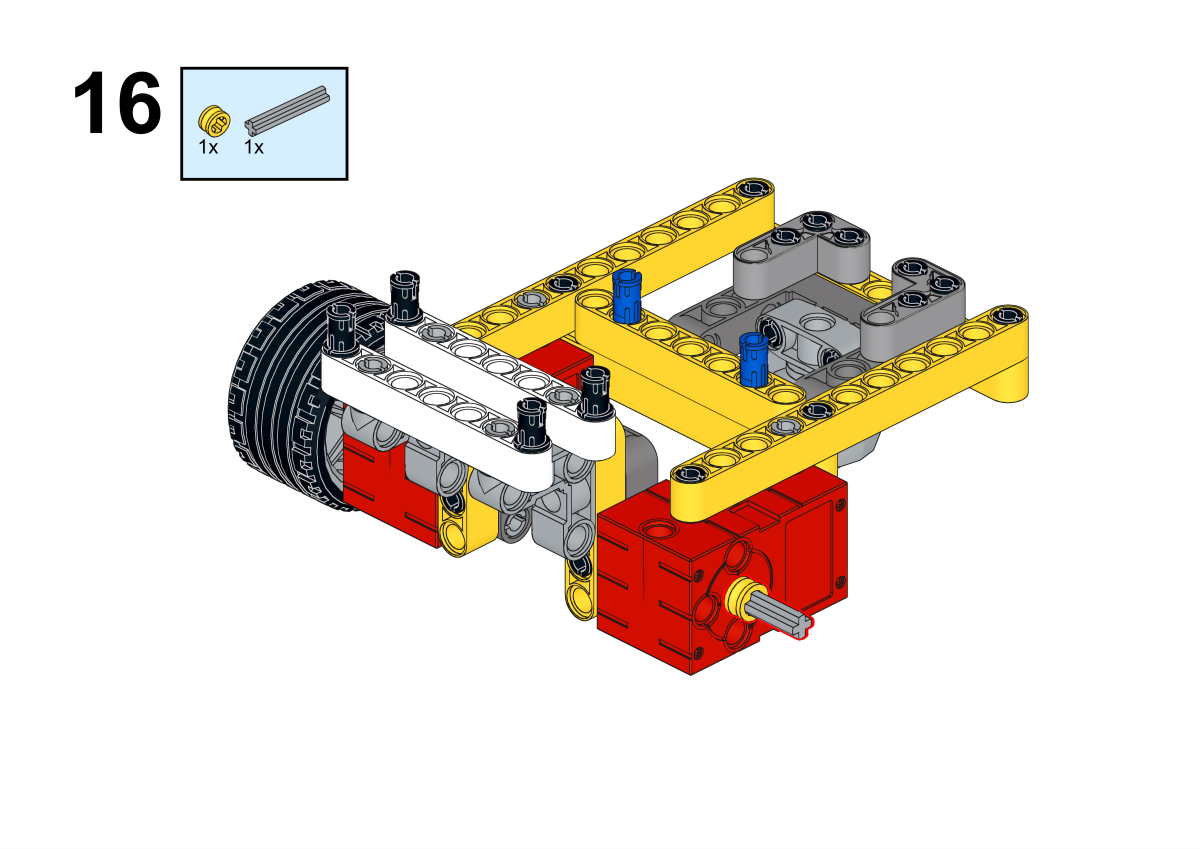
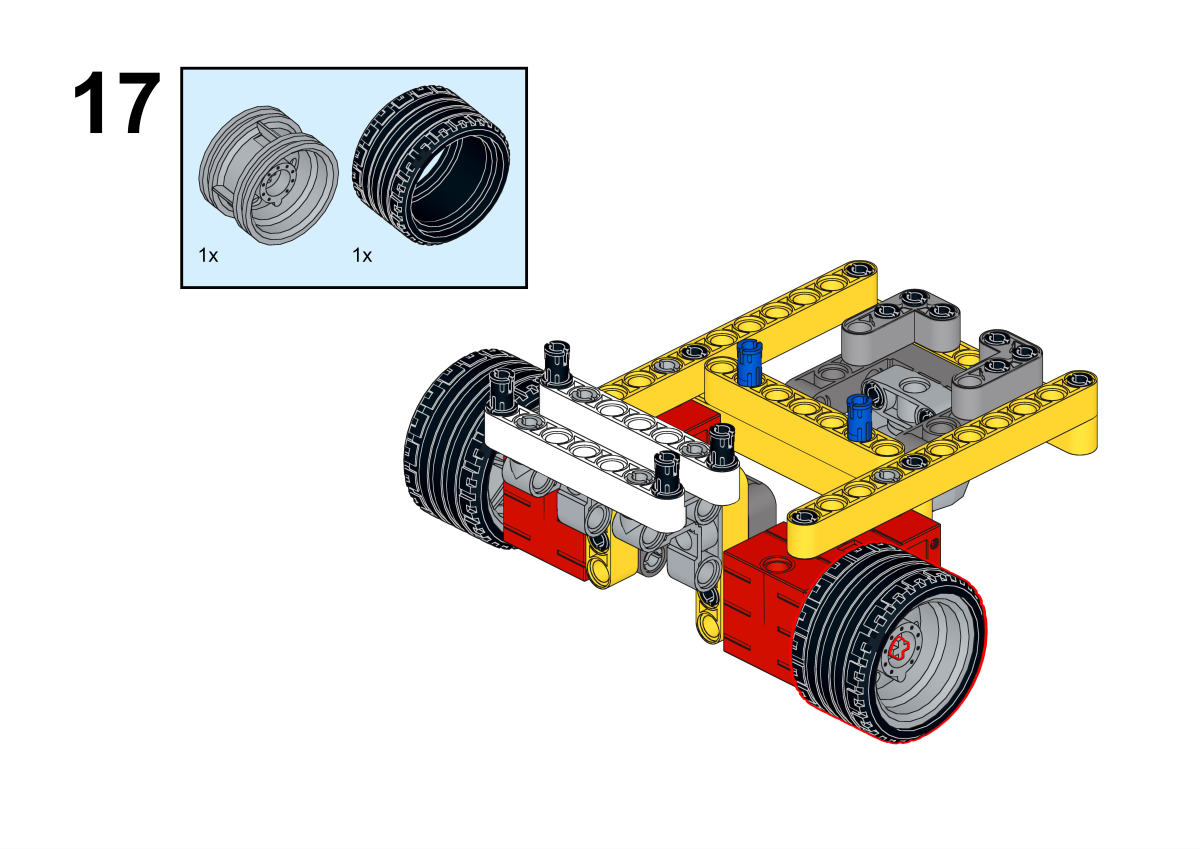

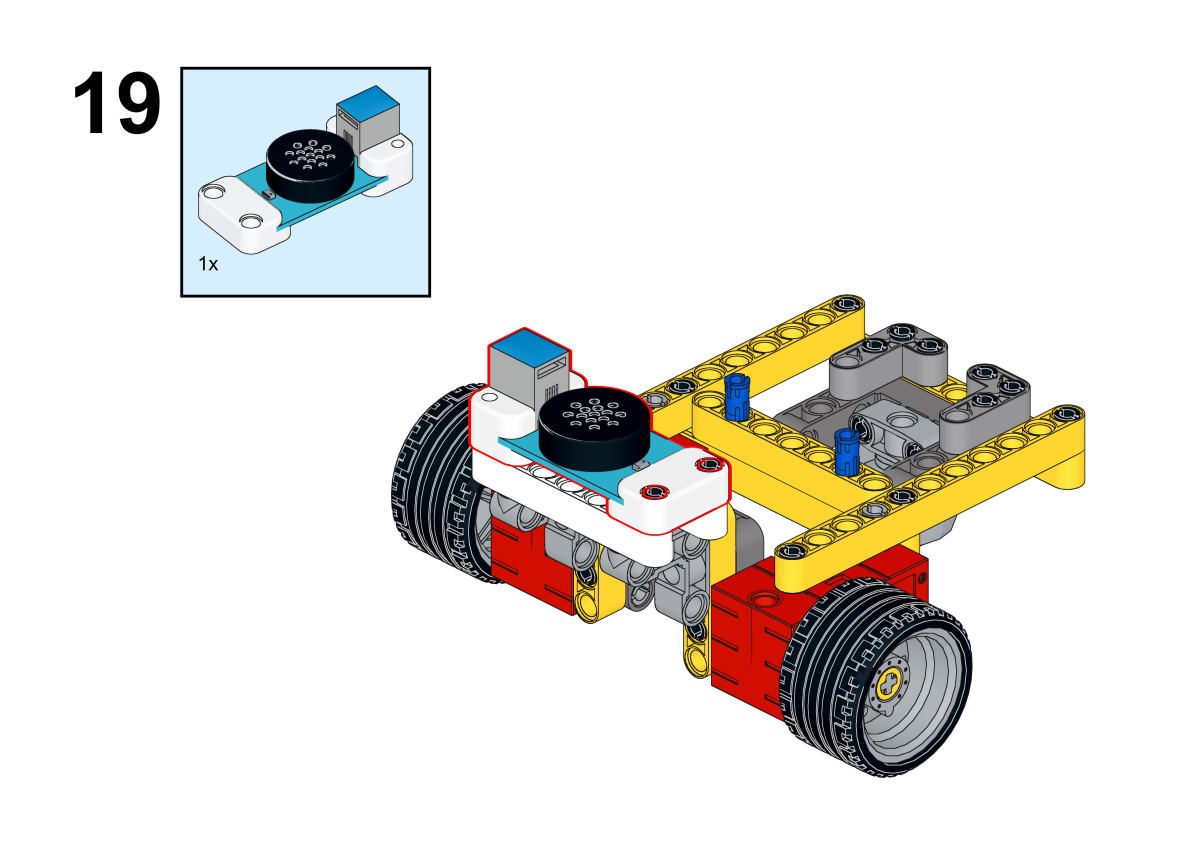

Completion of construction

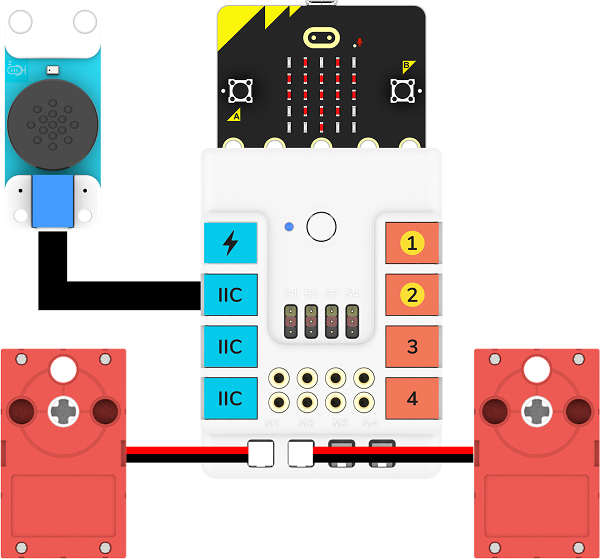
Hardware Connection
Connect the two motors to the M1 and M2 ports, and connect the voice recognition sensor to the IIC port.
Software Program
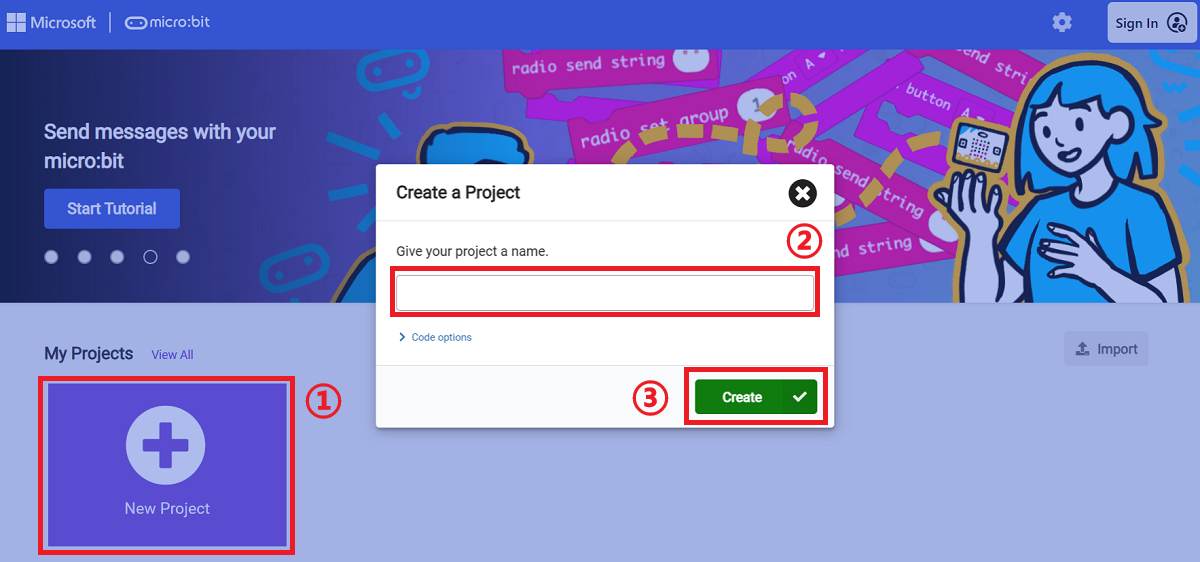
Open the program platform makecode
Create a new project
Click extensions
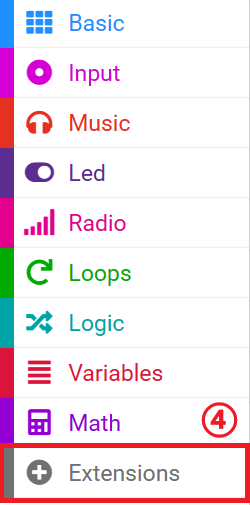
Search for nezha in the bar and add it.
Search for planetx in and add it.
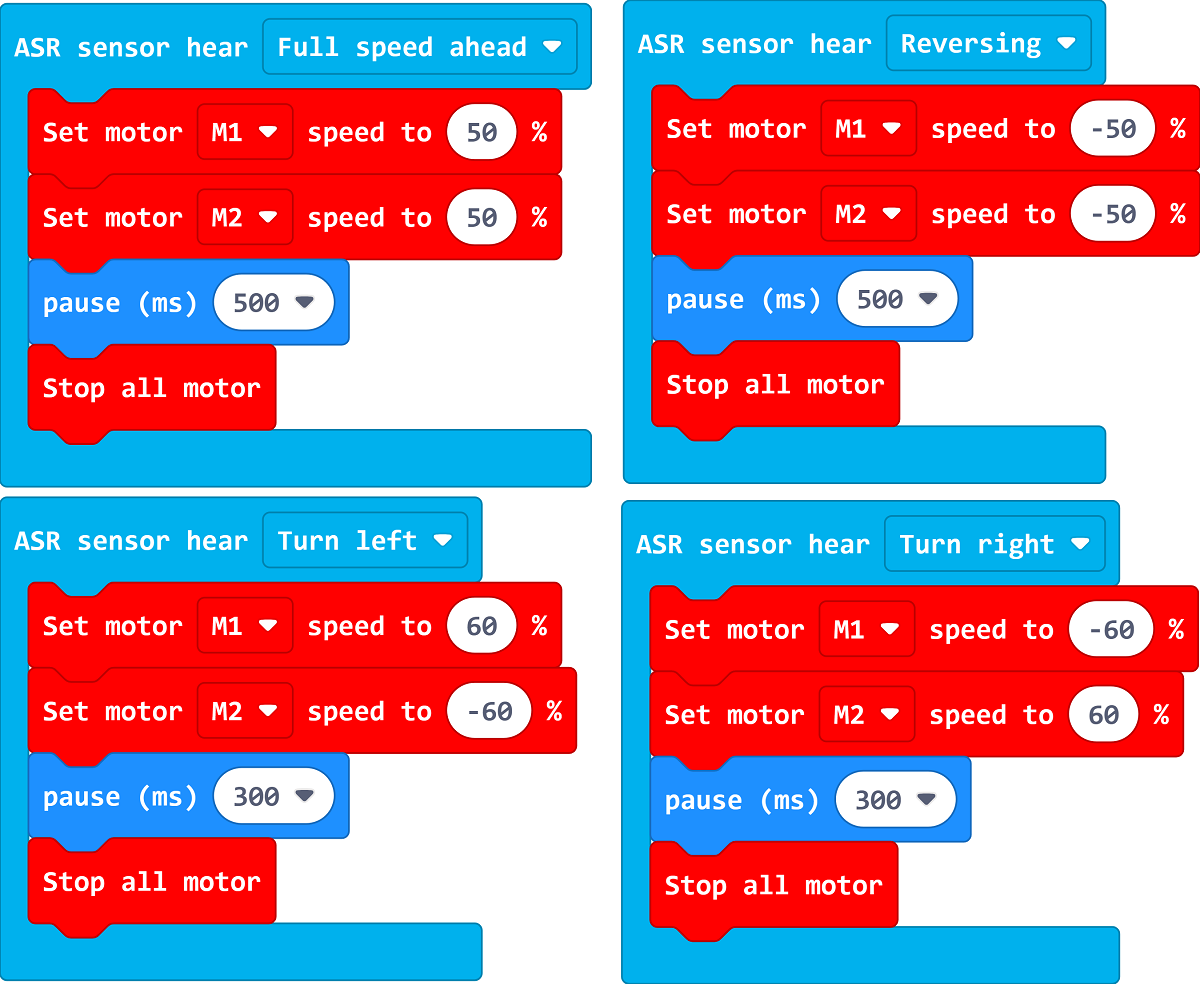
Write the program
Link: https://makecode.microbit.org/_CuVMyCEKA9Um
You can also download it in here.
Teamwork and Presentation
Students are divided into small groups and work together to create and program cases.
Students are encouraged to cooperate, communicate, and share their experiences with each other.
Each group has the opportunity to present the cases they have produced to the other groups.
Sample case effect
The trolley's route can be controlled by voice.

Reflection
Share in groups so that students in each group can share their production process and insights, summarize the problems and solutions they encountered, and evaluate their strengths and weaknesses.
Expanding Knowledge
The evolution of speech recognition technology
The development of speech recognition technology dates back to the mid-20th century and has gone through several phases and major breakthroughs, the following are the major milestones in its development:
1950s and 1960s:
Early speech recognition research focused on the fundamentals of simulating sound and the extraction of acoustic features. In 1952, Bell Labs researchers Davis and Biddulph developed the world's first speech recognition system, Audrey, which was capable of recognizing numbers. 1970s and 1980s:
This period saw significant advances in speech recognition technology, including more sophisticated acoustic feature extraction methods and pattern matching algorithms. The Hidden Markov Model (HMM) was introduced and became the standard in speech recognition. In 1971, IBM researchers developed Shoebox, the first commercial speech recognition system for recognizing numbers. 1990s:
As computer performance increased and more research was invested, the accuracy of speech recognition improved significantly. Statistical language models are introduced to improve the contextual understanding of recognition results. More commercially available speech recognition systems appear for use in telephone systems and automated customer service. Early 21st century:
A major breakthrough in speech recognition occurs with the rise of deep learning techniques. Deep neural networks (DNNs) were used for acoustic modeling, greatly improving accuracy. In 2009, Microsoft introduced the Xbox Kinect, a system with speech recognition capabilities, marking the adoption of speech recognition technology in consumer electronics. Recent years:
Since the 2010s, the further development of deep learning techniques and the availability of big data have led to huge breakthroughs in speech recognition. Cloud computing and artificial intelligence platforms (e.g., Amazon's Alexa, Apple's Siri, Google's Google Assistant, etc.) have made speech recognition a common technology in daily life for smart assistants, smart homes, car navigation, and other areas. Open source projects (e.g., CMU Sphinx, Kaldi, etc.) and cloud-based APIs have made it easier for developers to build and integrate speech recognition features. Overall, the evolution of speech recognition technology has gone through a number of key periods, from the early days of acoustic feature extraction to the introduction of Hidden Markov Models to the application of Deep Learning, which has continued to improve accuracy and usability and become an integral part of modern technology. In the future, as technology continues to evolve, speech recognition technology will continue to play an important role in various fields.