Case 07 The Crawling Robot
Introduction
Crawling is a common form of locomotion in the animal world. We can observe that many animals such as snakes, spiders and geckos have a unique way of crawling. They move forward through coordinated body movements, contraction and extension of their muscles and friction with the ground. The way these animals crawl has a certain regularity, but also shows their individual characteristics and flexibility.
The aim of this course is to introduce students to the principles of motor control and the application of gearing by creating an example of a crawling robot. Students will use the materials in Nezha Inventor's Kit V2 to build a crawling robot and learn how to achieve the crawling action of the robot by controlling the motors and gearing. Through this project, students will develop creativity, problem solving skills and teamwork spirit.

Teaching Objectives
- Understand the working principles and control methods of electric motors.
- Understand the basic principles and applications of gearing.
- Learn to build the basic structure of a crawling robot using the materials in Nezha Inventor's Kit V2.
- Understand the effect of gearing on the crawling action of the robot and make adjustments and optimisations.
- Develop creativity, problem solving skills and teamwork spirit.
Teaching Preparation
[Nezha Inventor's Kit V2] (https://www.elecfreaks.com/nezha-inventor-s-kit-v2-for-micro-bit.html)
Teaching Process
Introduce
Students are introduced to the background and objectives of crawling robot building to stimulate their interest and curiosity.
Today we will enter an exciting world of exploration - mimicking crawling. Imagine being able to create a robot that can crawl as gracefully as real animals, mimicking their movements and mannerisms. In this project, we will explore how knowledge of science and engineering can be used to create robots that can mimic reptiles.
Crawling is a common form of locomotion in the animal world. We can observe that many animals such as snakes, spiders and geckos have a unique way of crawling. They move forward through coordinated body movements, contraction and extension of their muscles, and friction with the ground. The way these animals crawl has a certain regularity, but also shows its own characteristics and flexibility.
In this project, we will attempt to imitate the crawling movements of animals by designing and building a robot that can simulate their movements. Using the materials in Nezha Inventor's Kit V2, we will build the structure of the robot and control its movement by means of a motor. At the same time, we will learn and apply the principles of gearing to achieve coordinated movements and crawling motions of the robot.
Through this project, we will not only learn and practice science and engineering, but also develop creativity, problem solving skills and teamwork spirit. We will explore the way reptiles move and apply this to robot design. We are sure you will have fun in the process and enhance your abilities in the process of exploration.
Let's embark on this innovative journey together, exploring the mysteries of the animal world and creating our own crawling mimicking robots!
Exploration
Discuss in groups and get students thinking about how to make a crawling robot from block materials, focusing on the basic principles of gearing.
- What factors need to be considered when making a robot to imitate an animal crawling?
- What is the role of gearing for a crawling robot?
Practice
Work in groups to create a crawling robot from block materials according to your own design.
Follow your own design to create a robot that imitates an animal crawling with block materials.
Examples
Assembly Steps
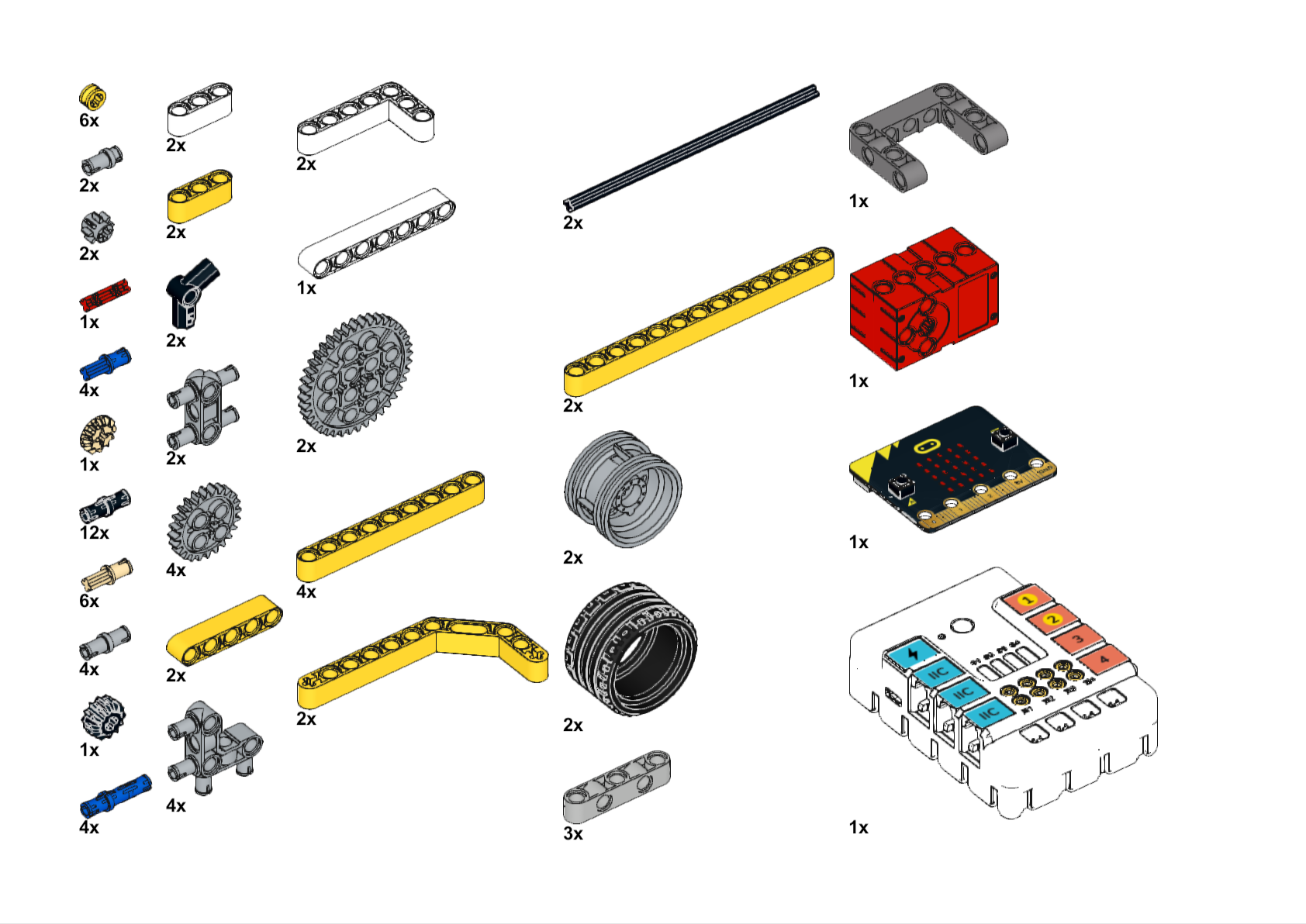
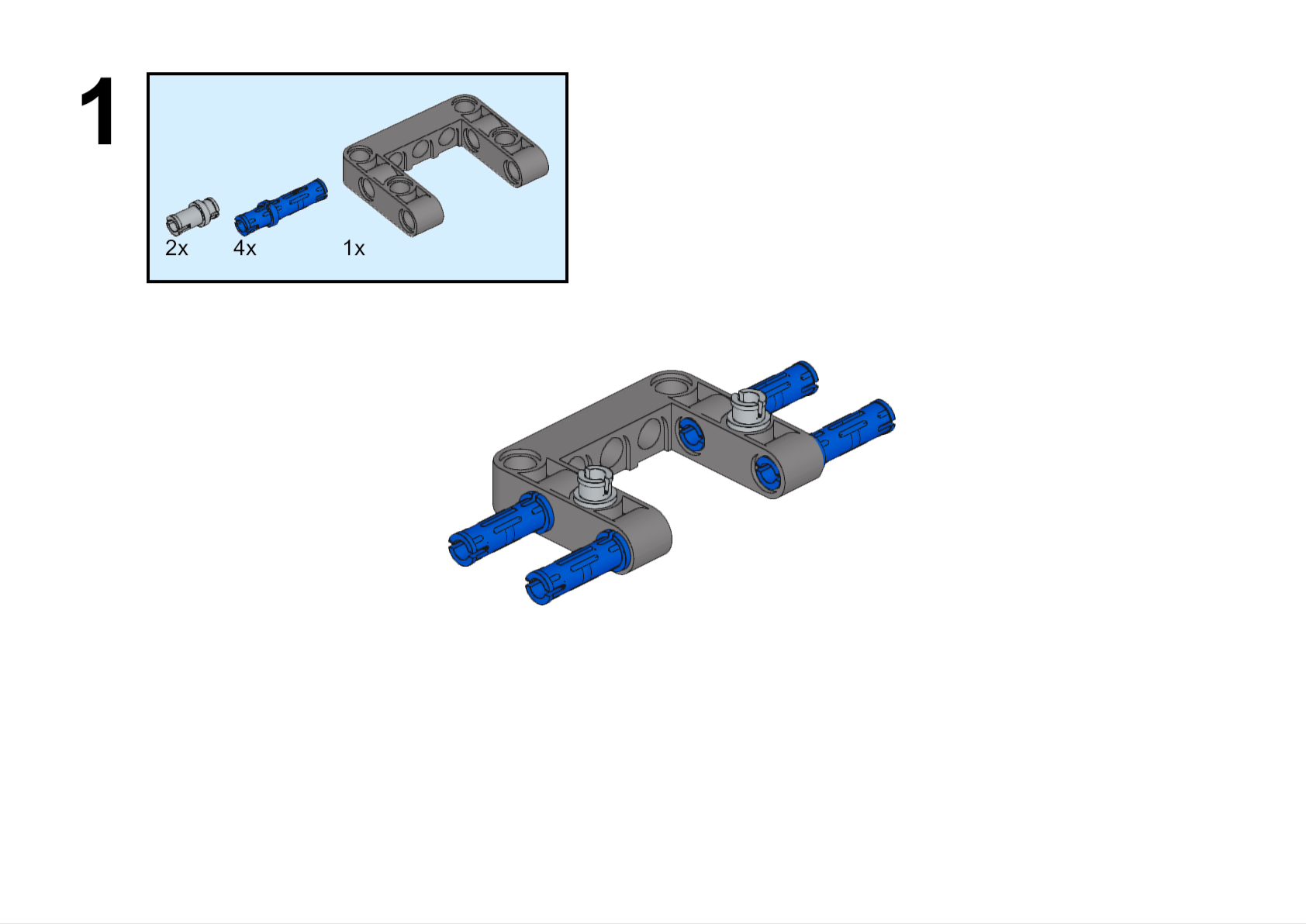
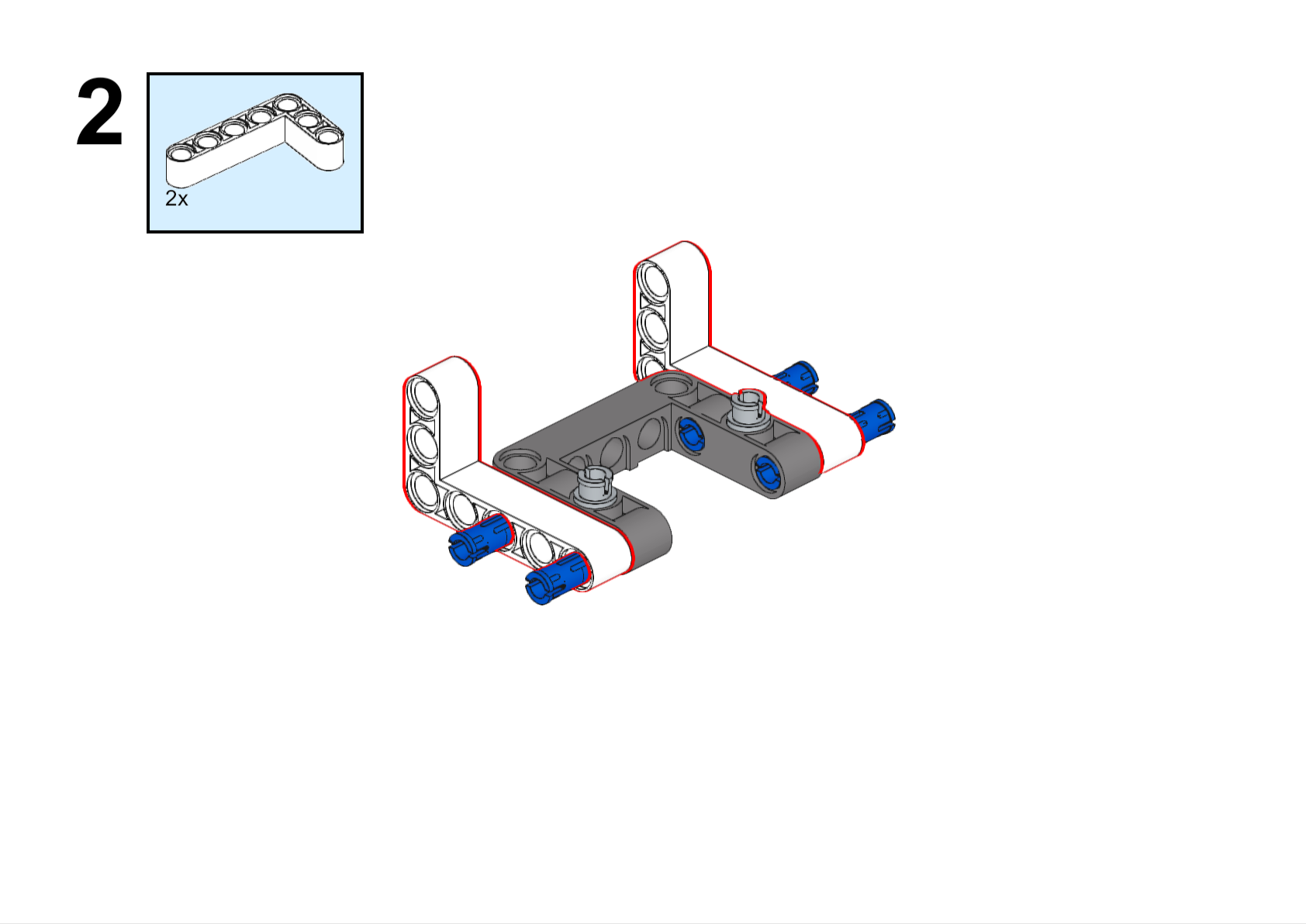
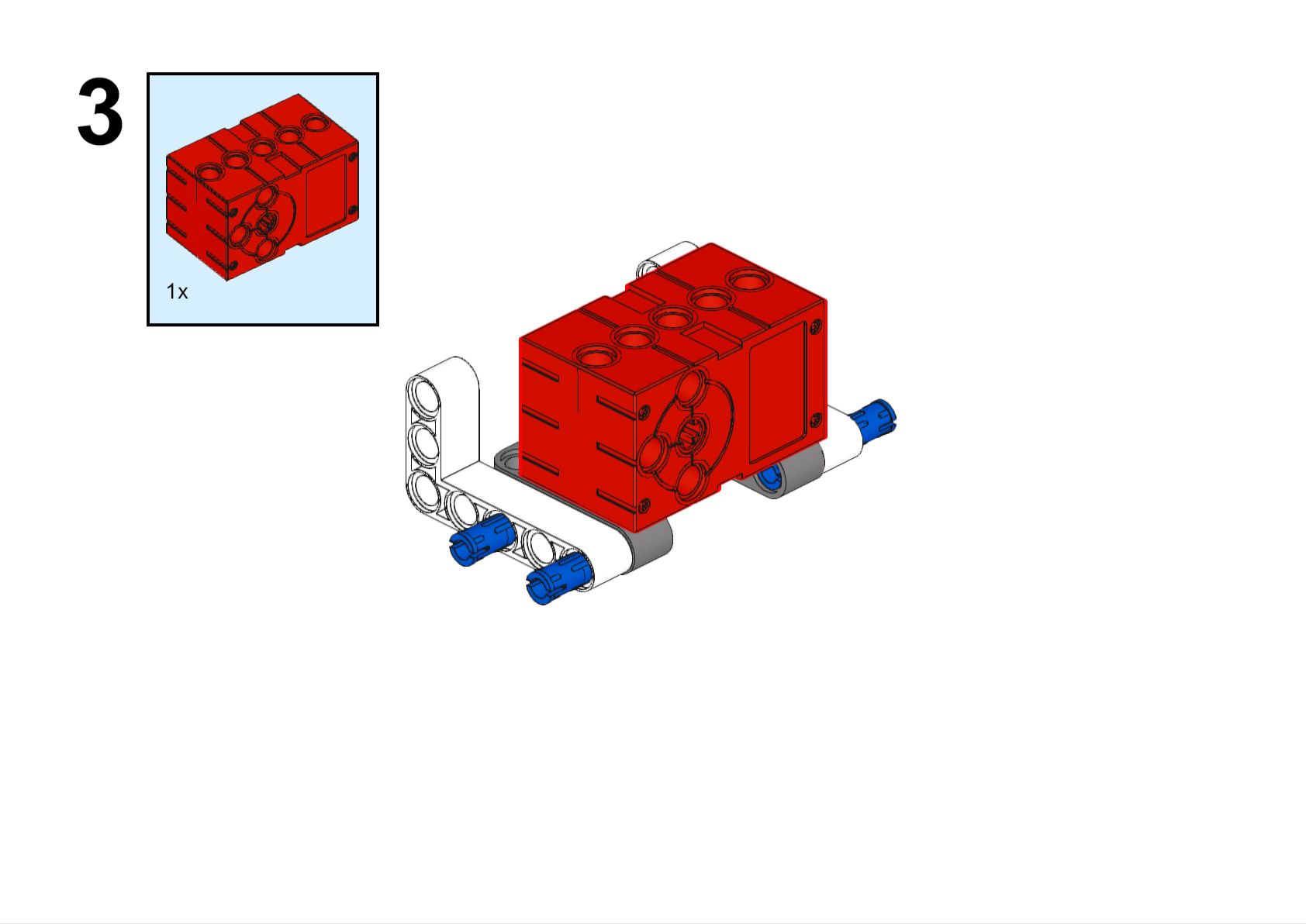
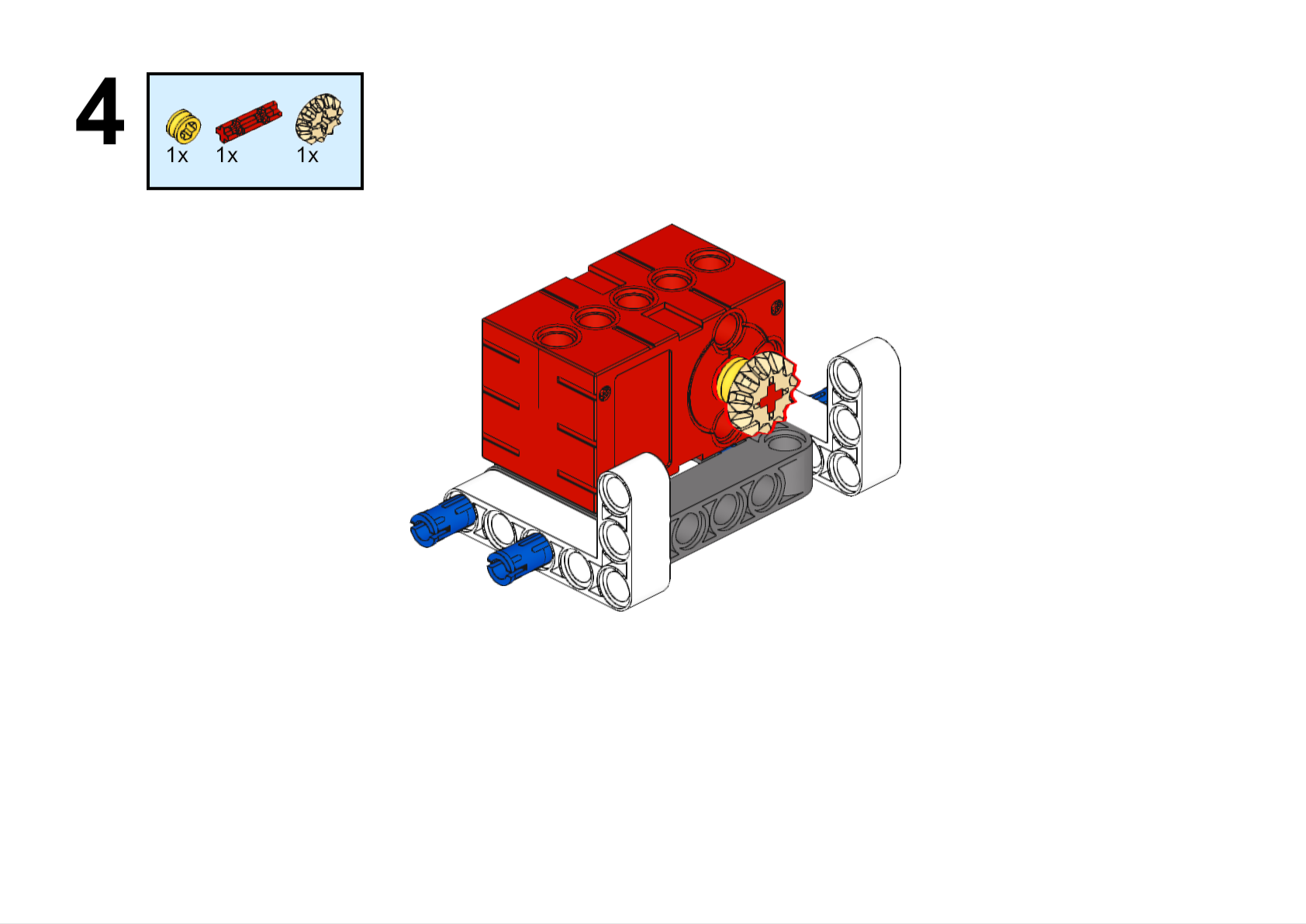
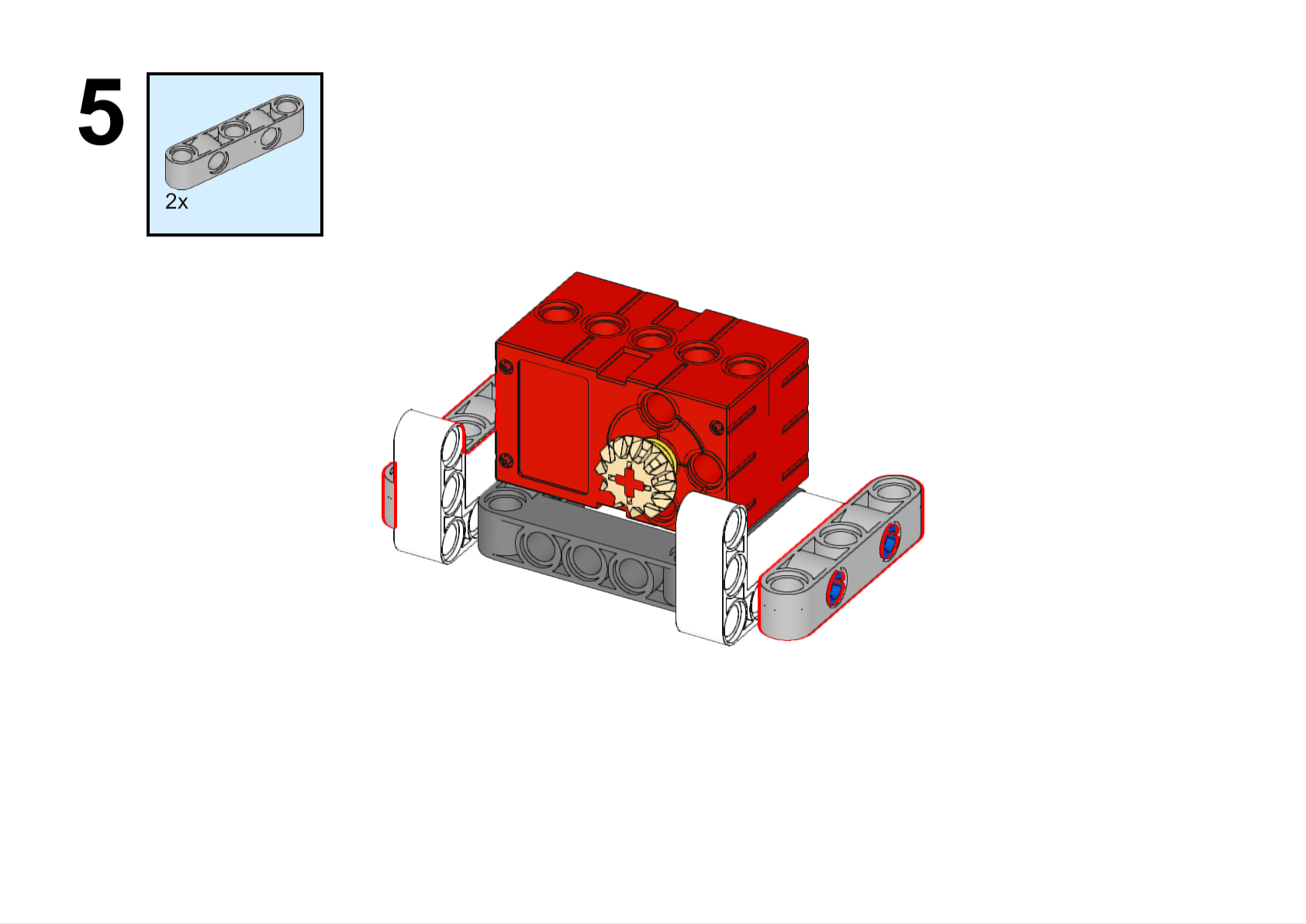
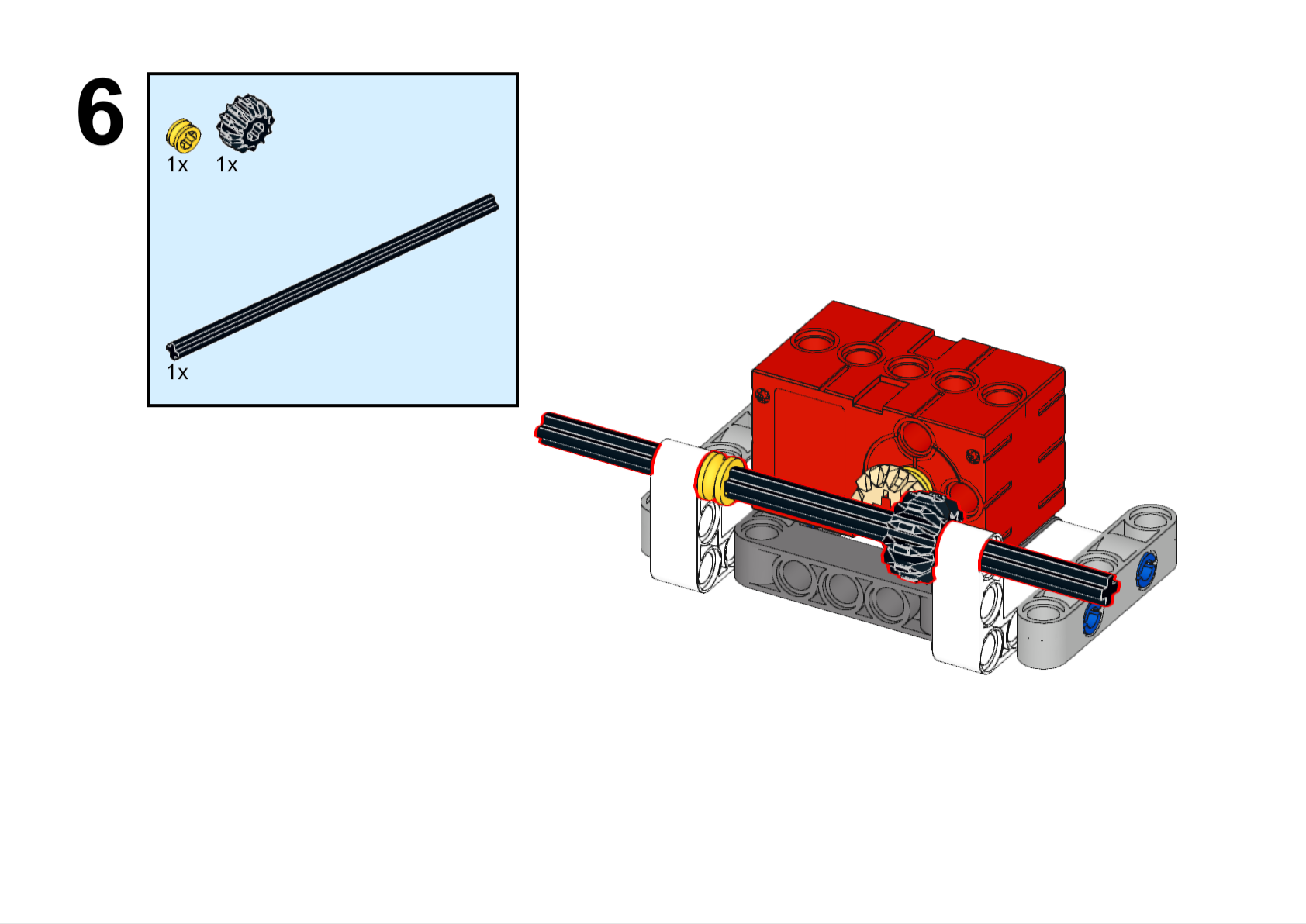
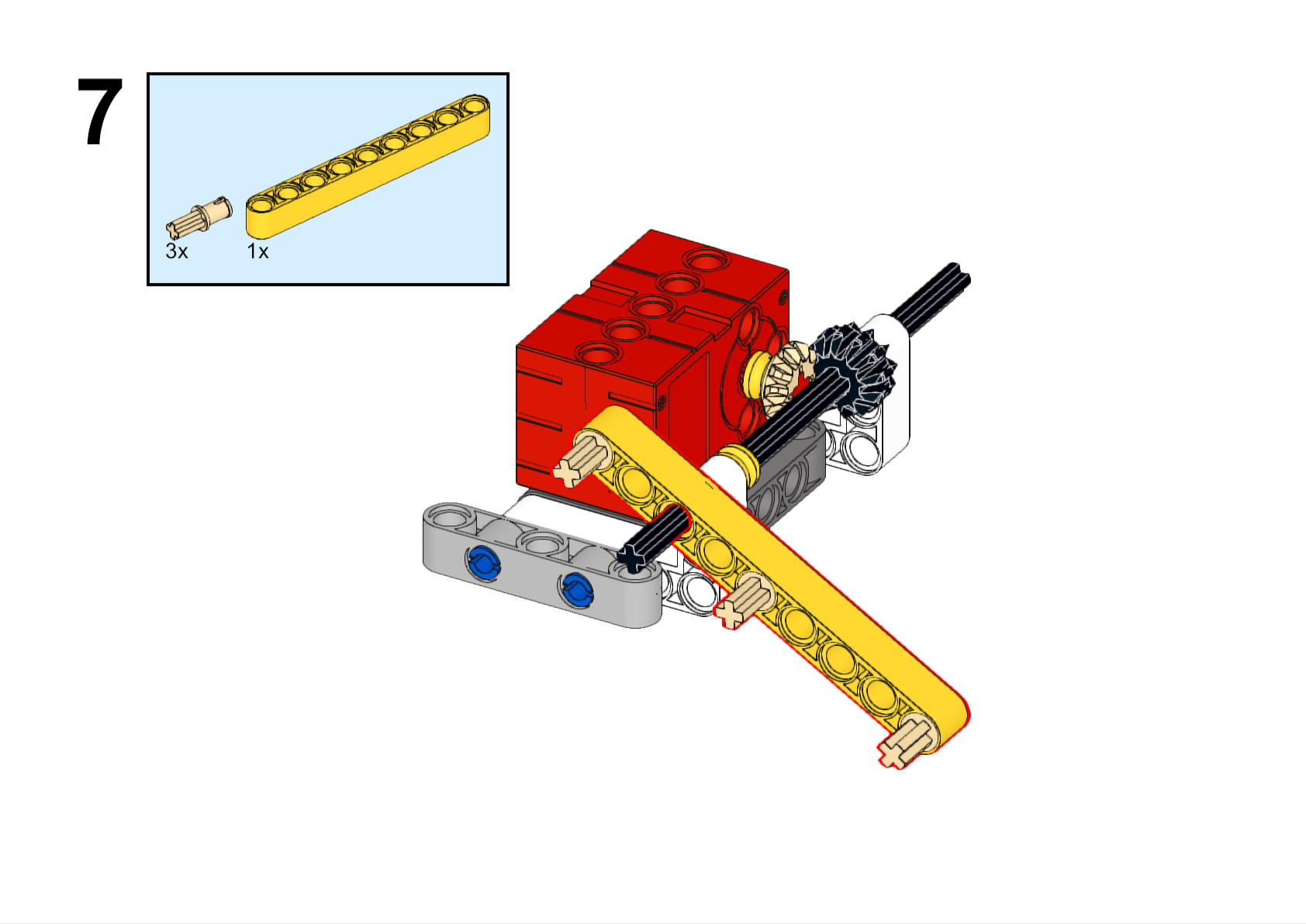
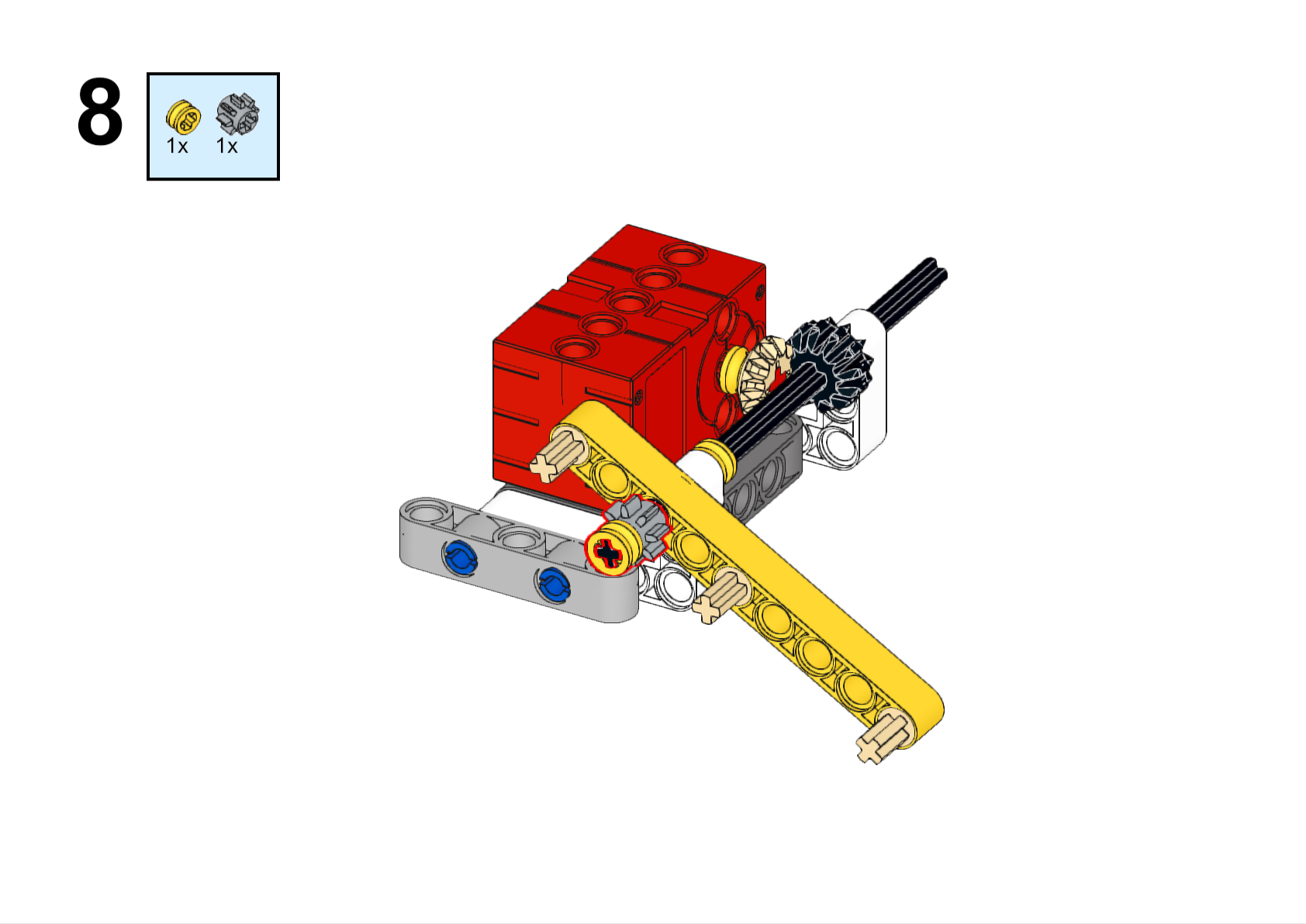
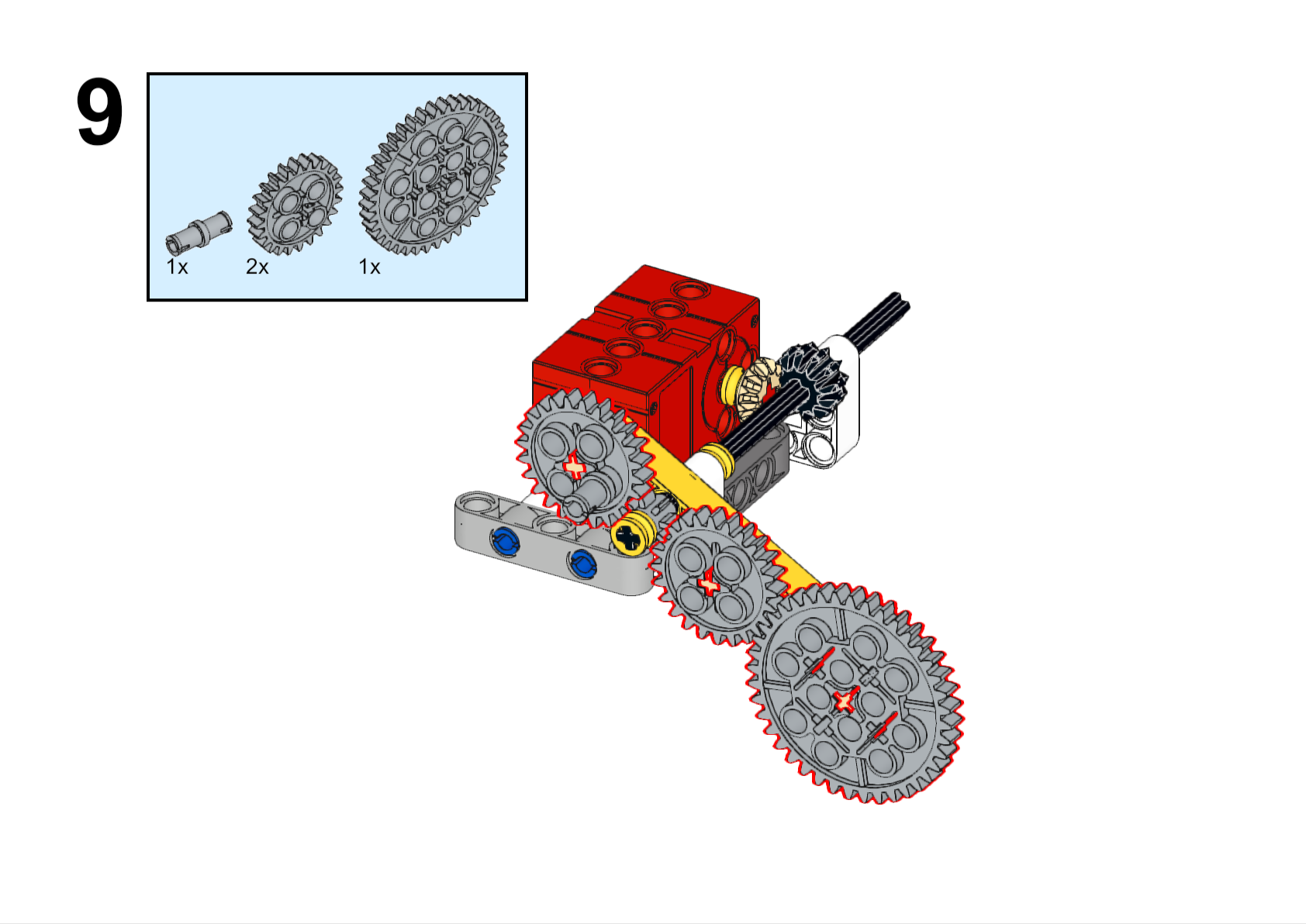
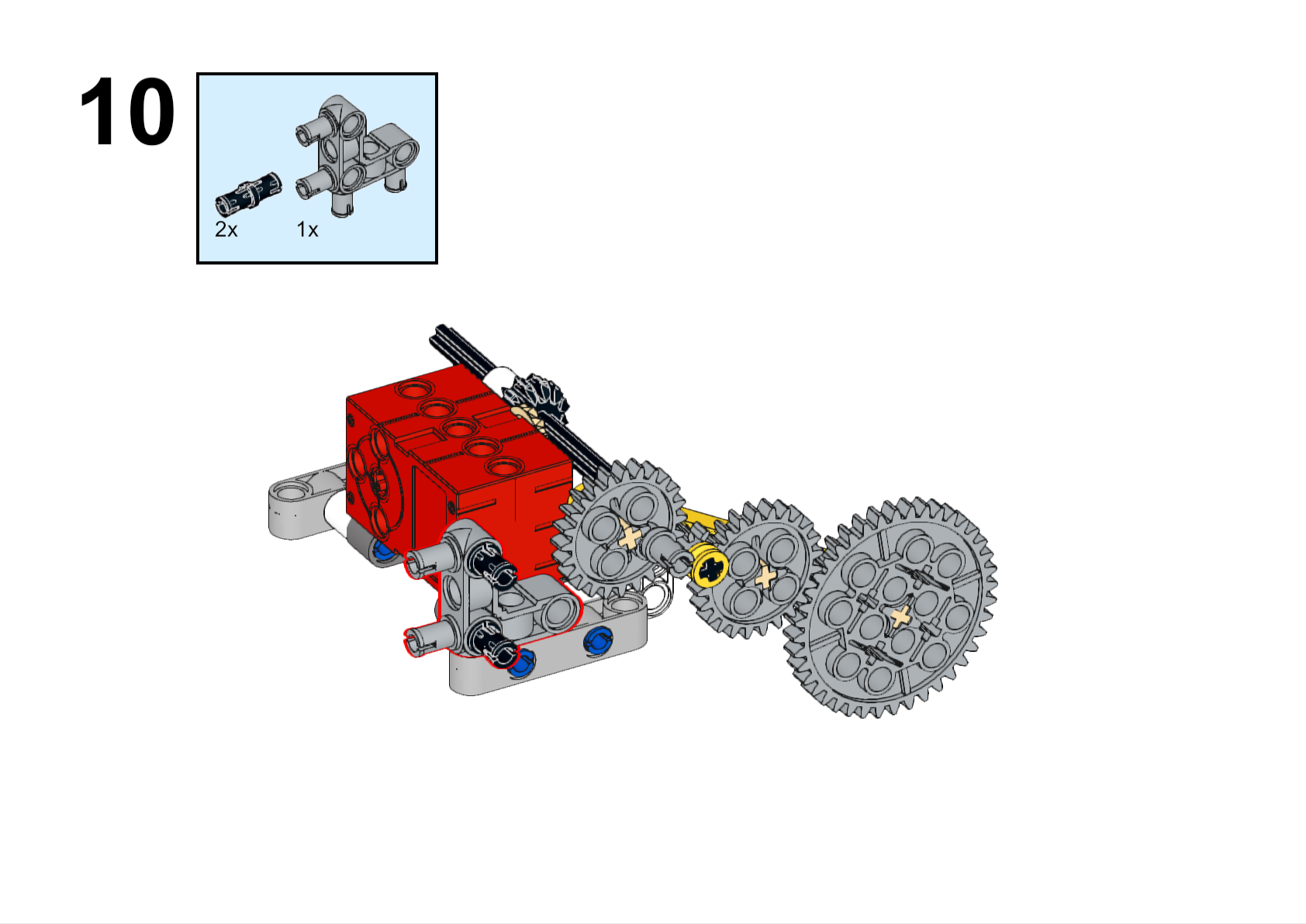
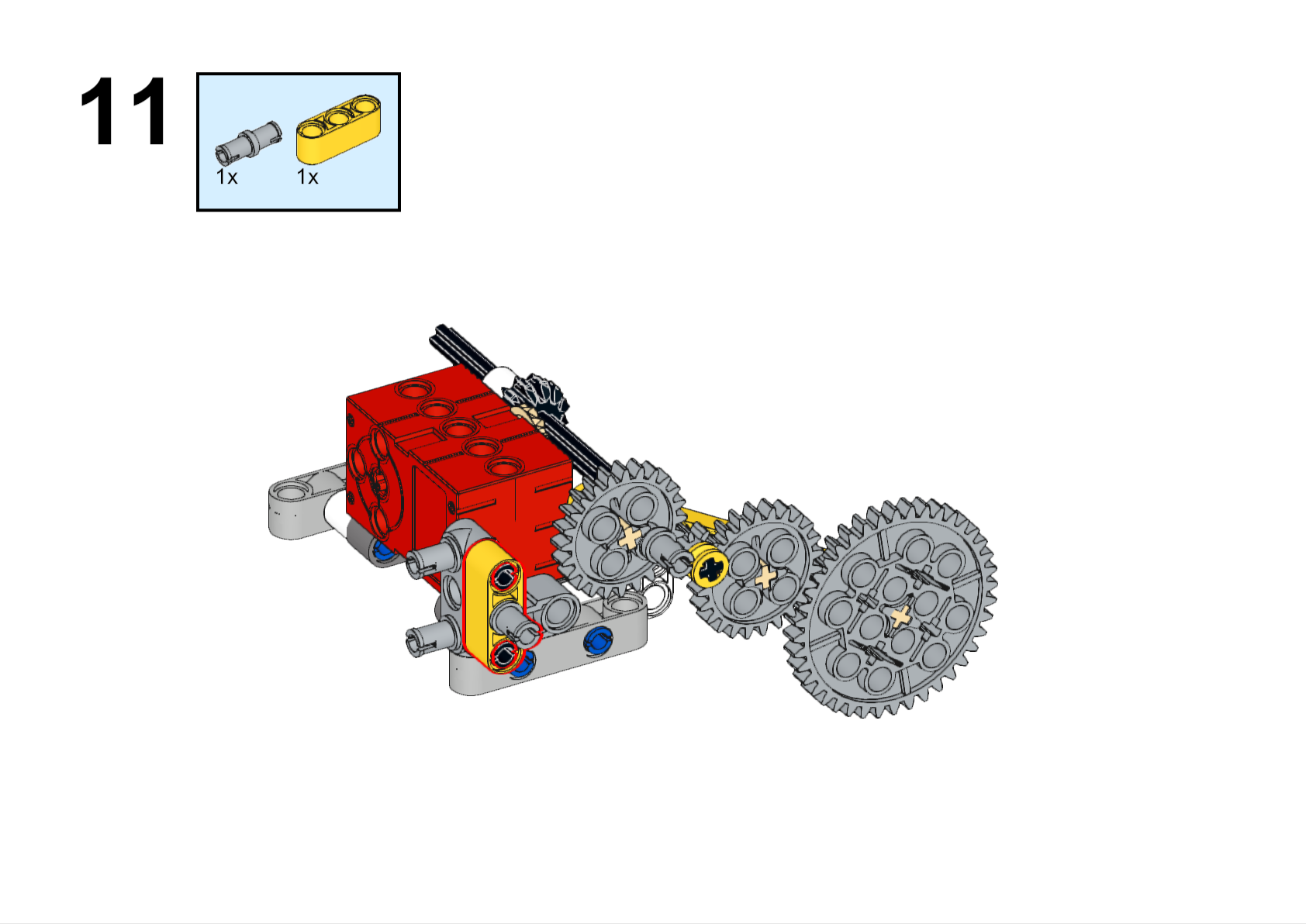
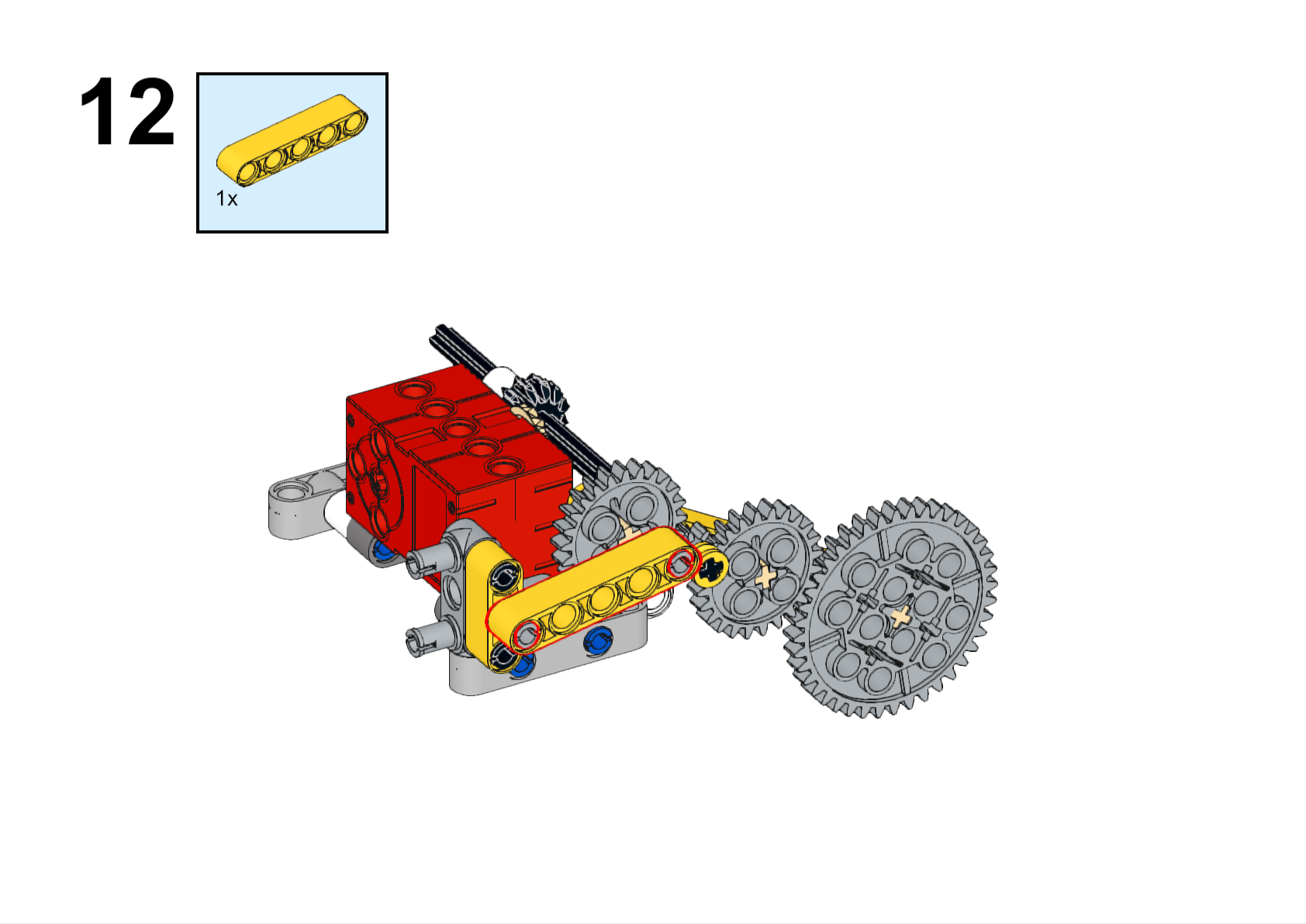
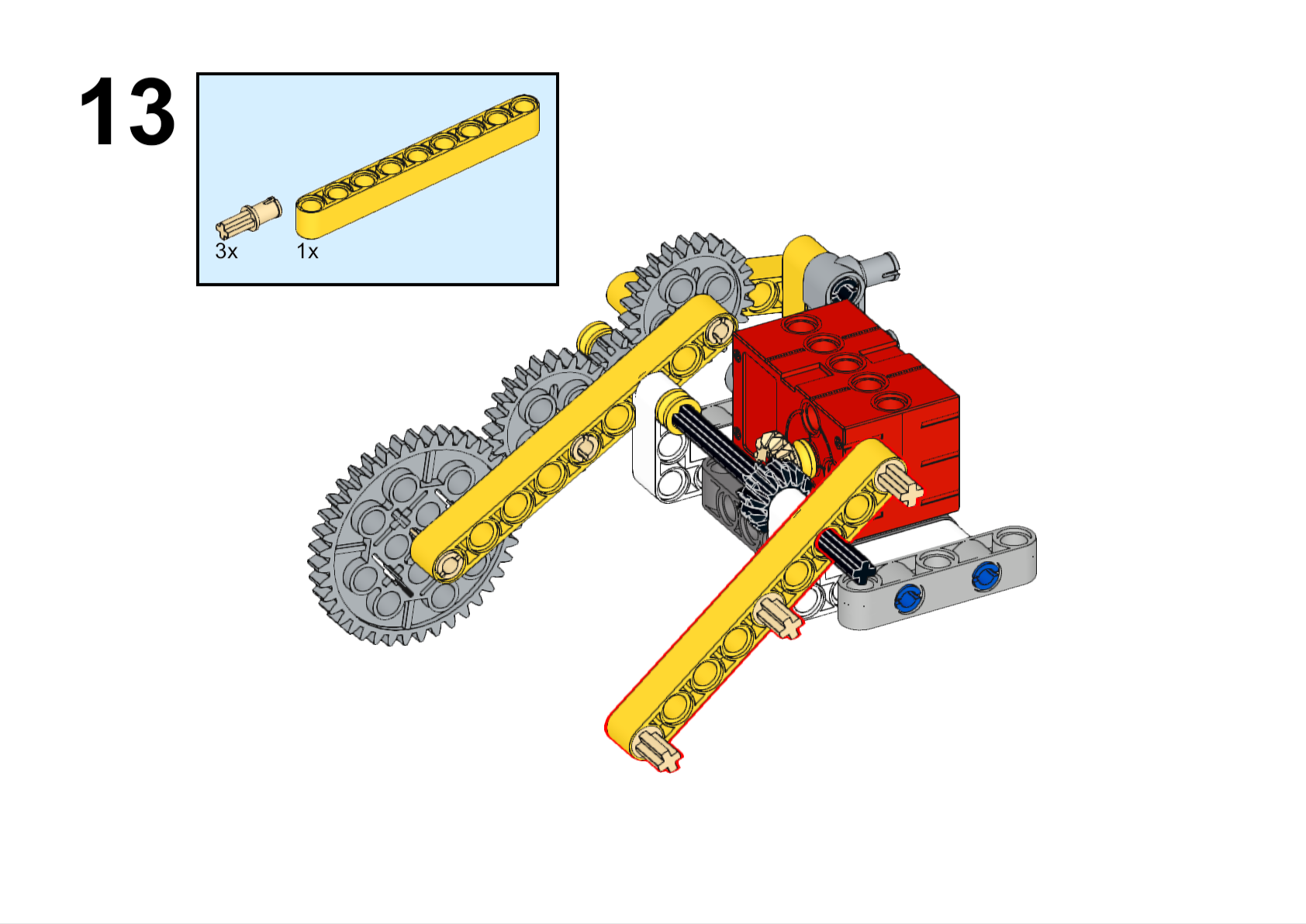
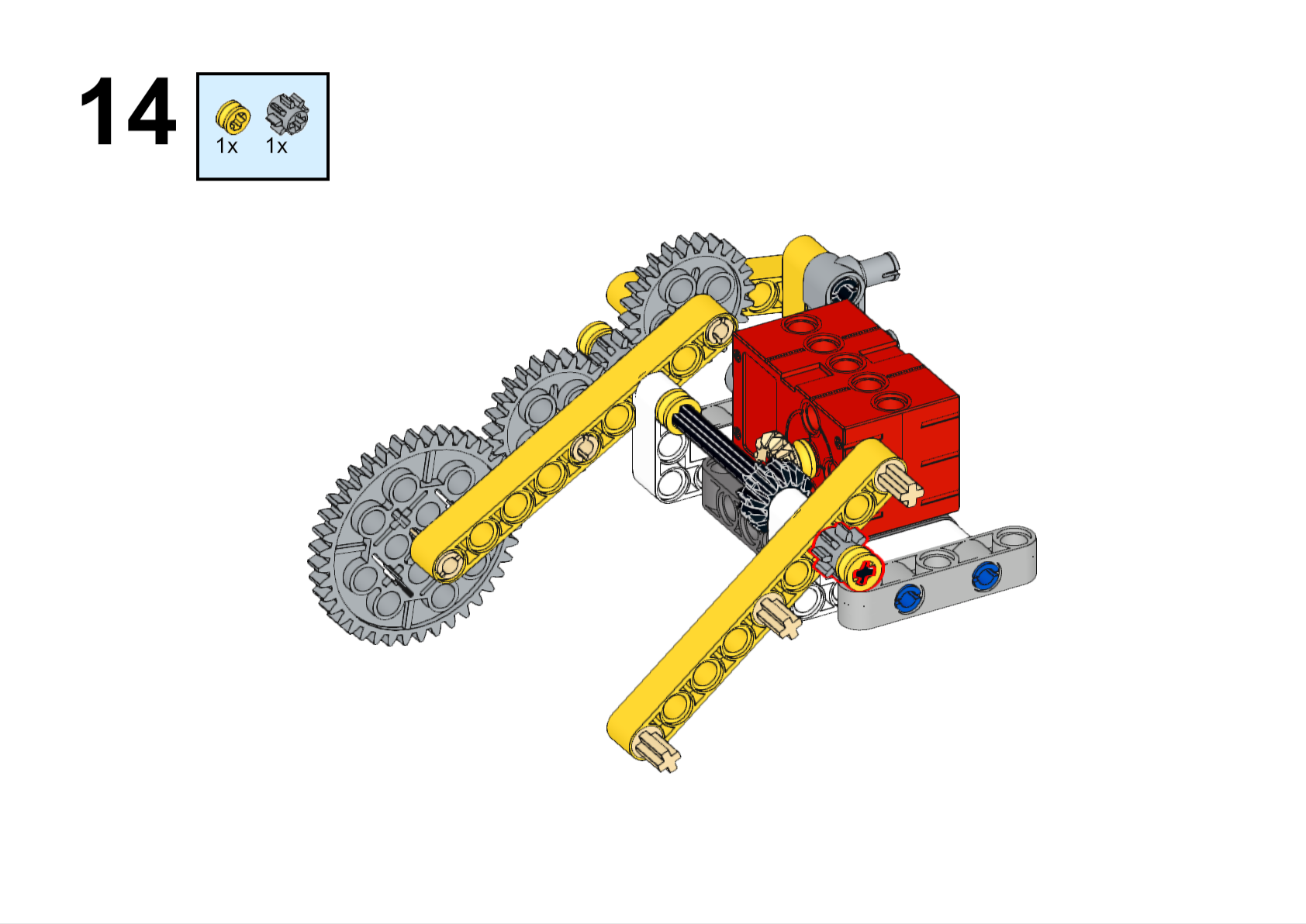
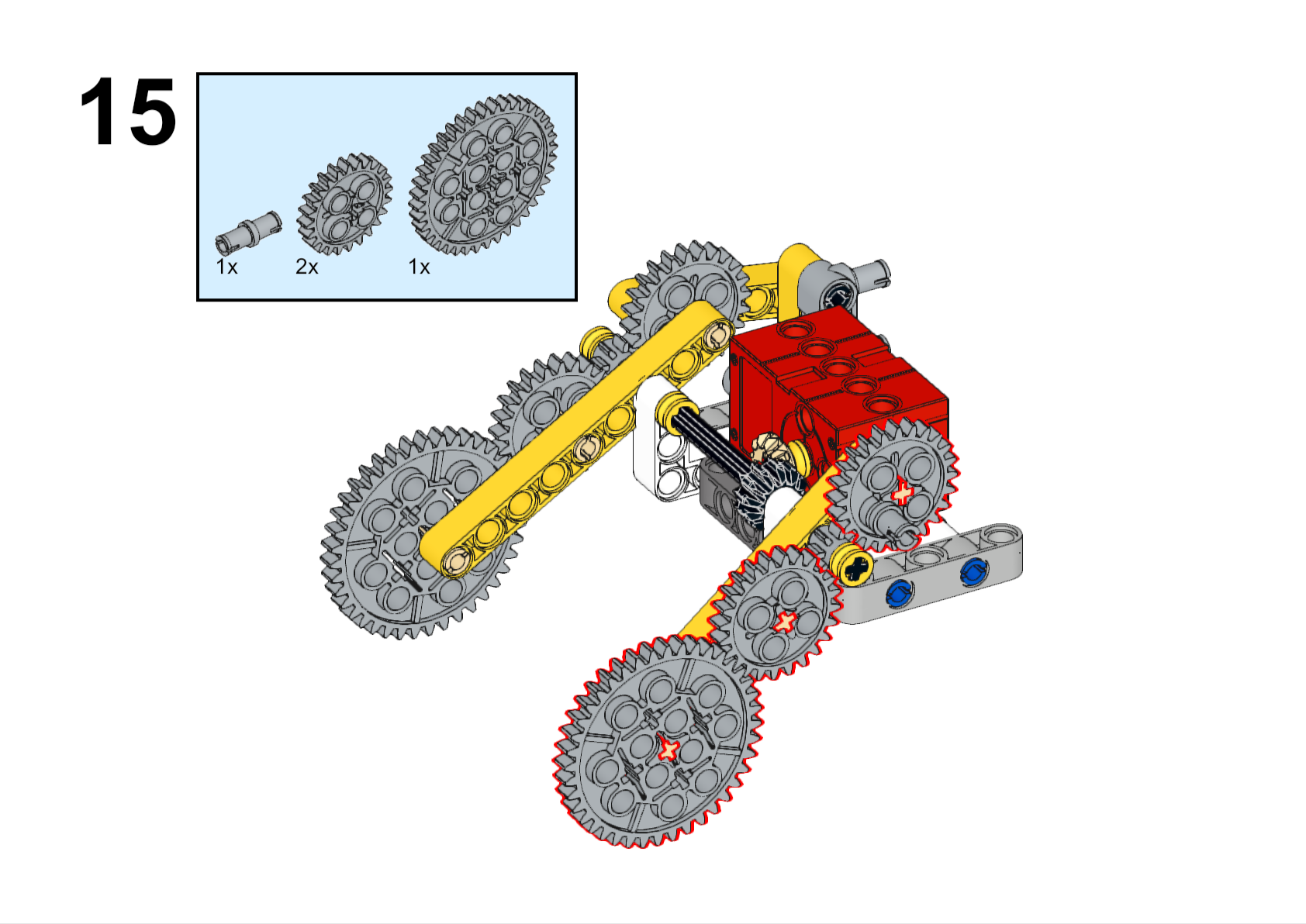
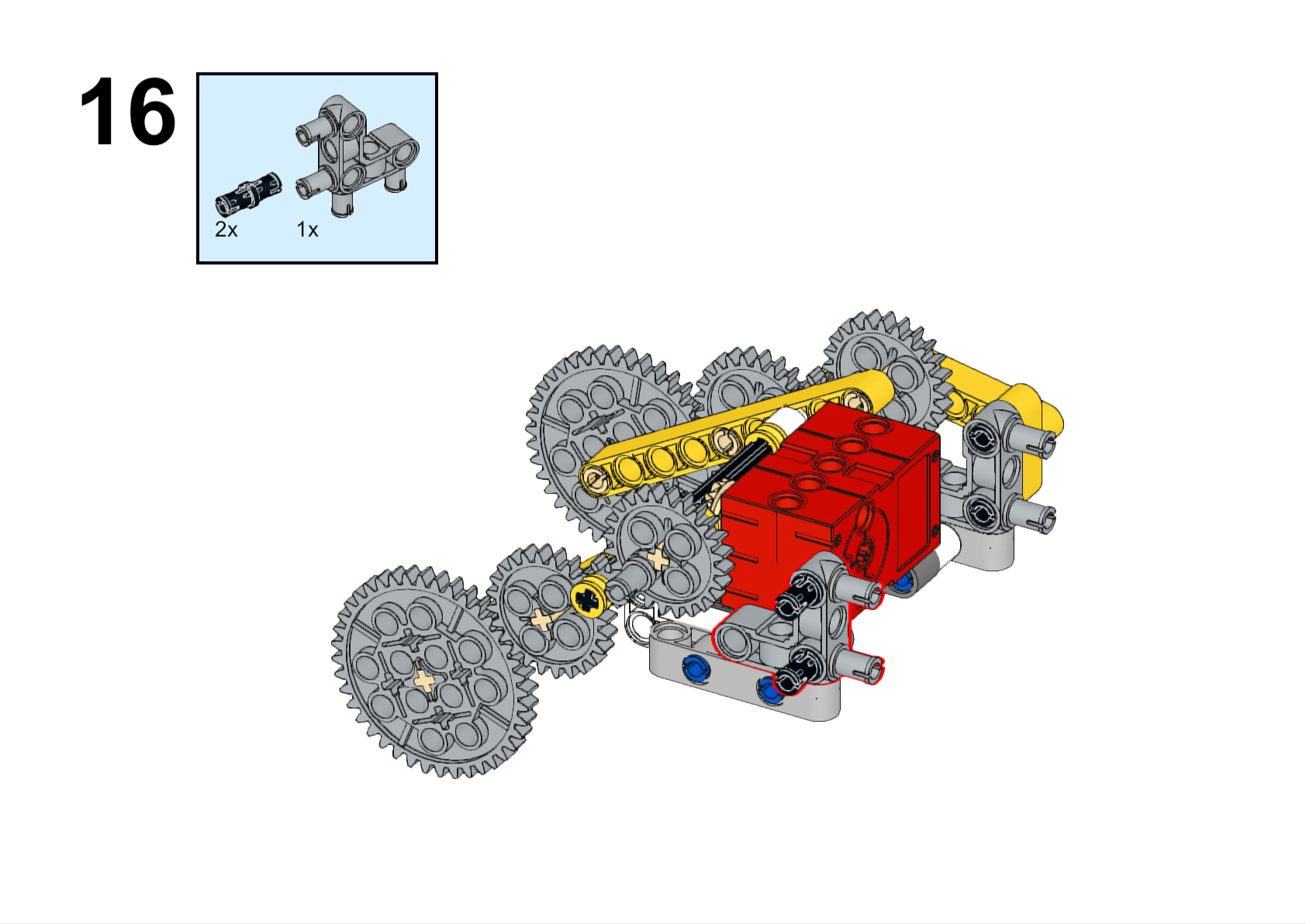
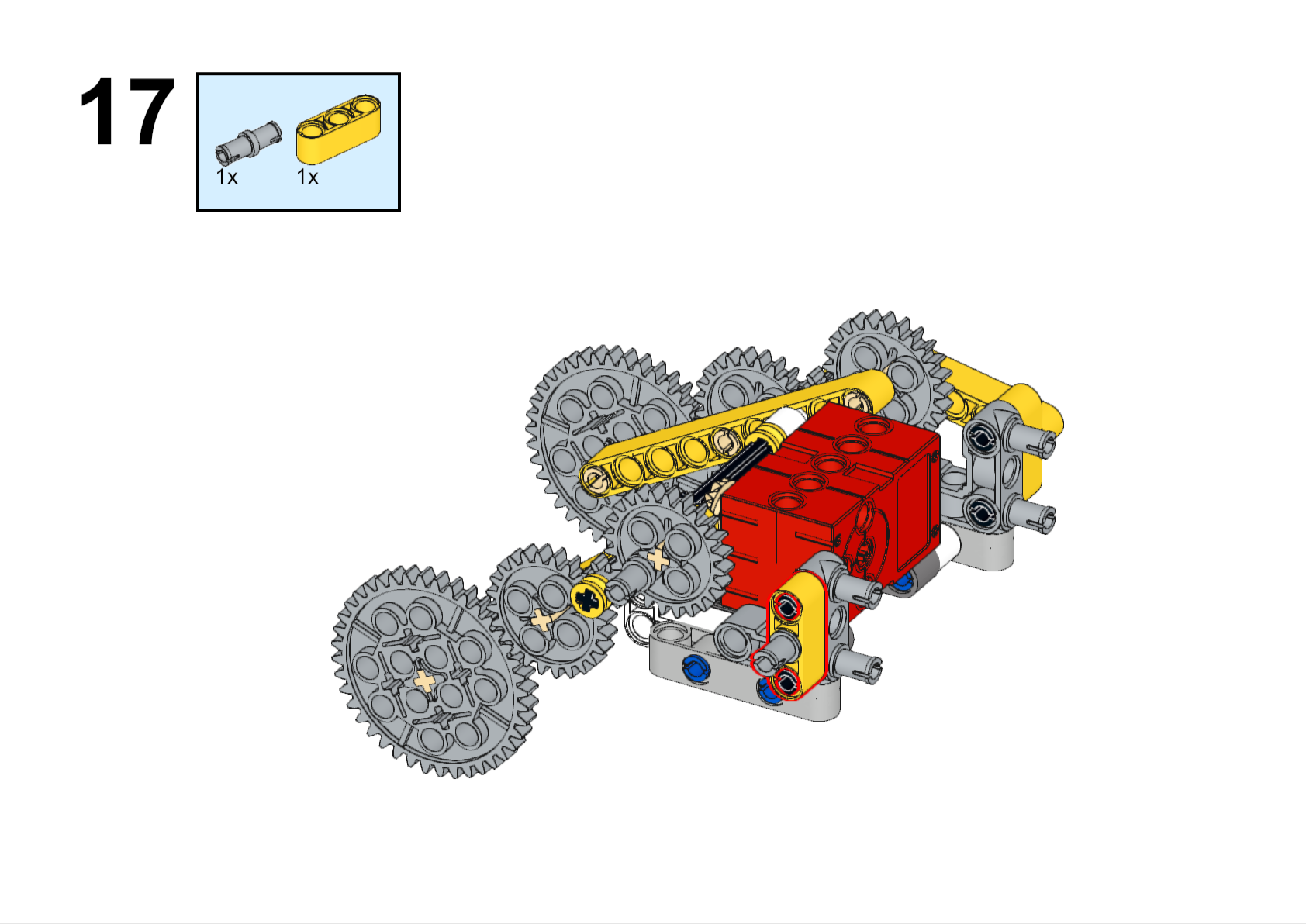
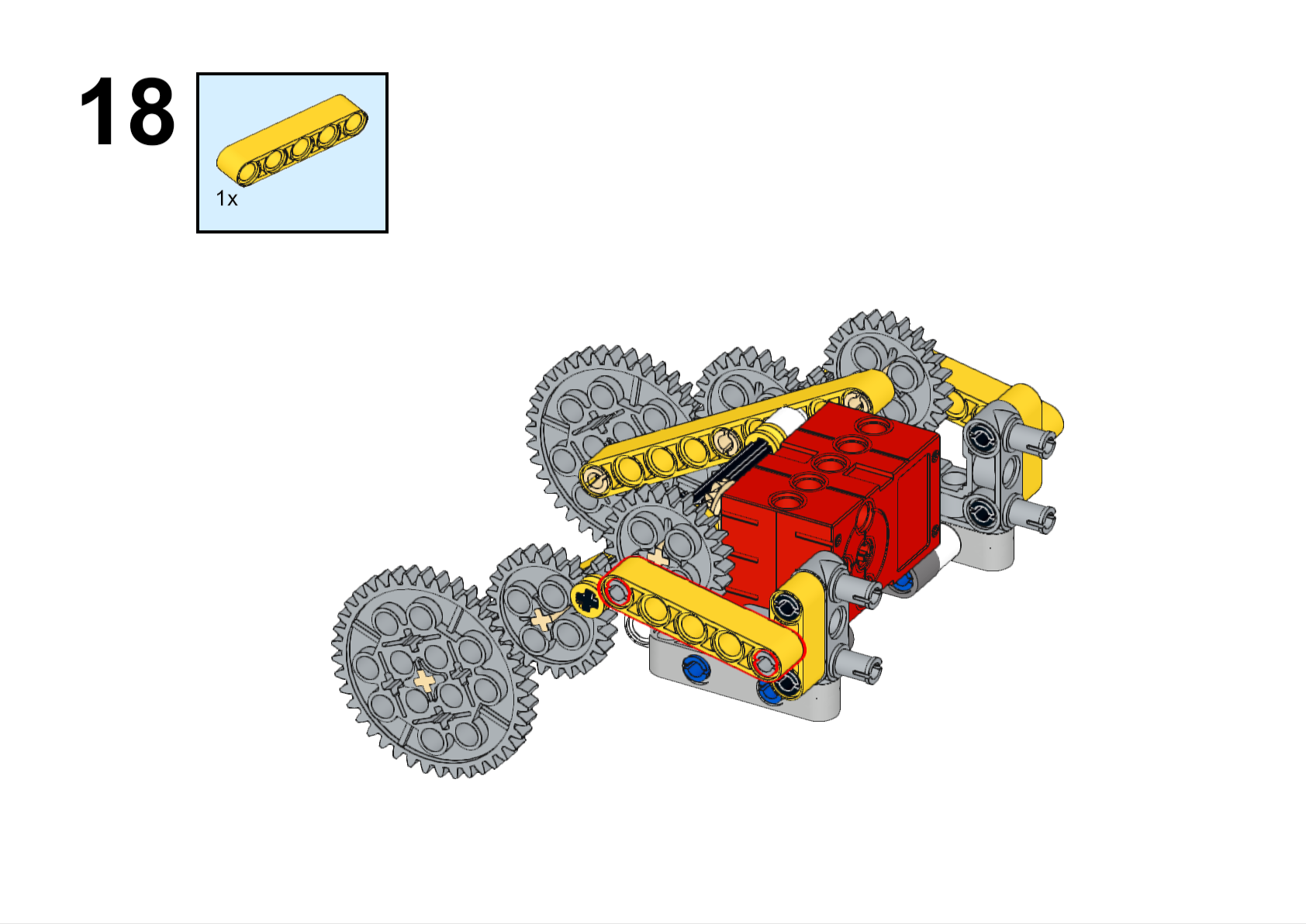
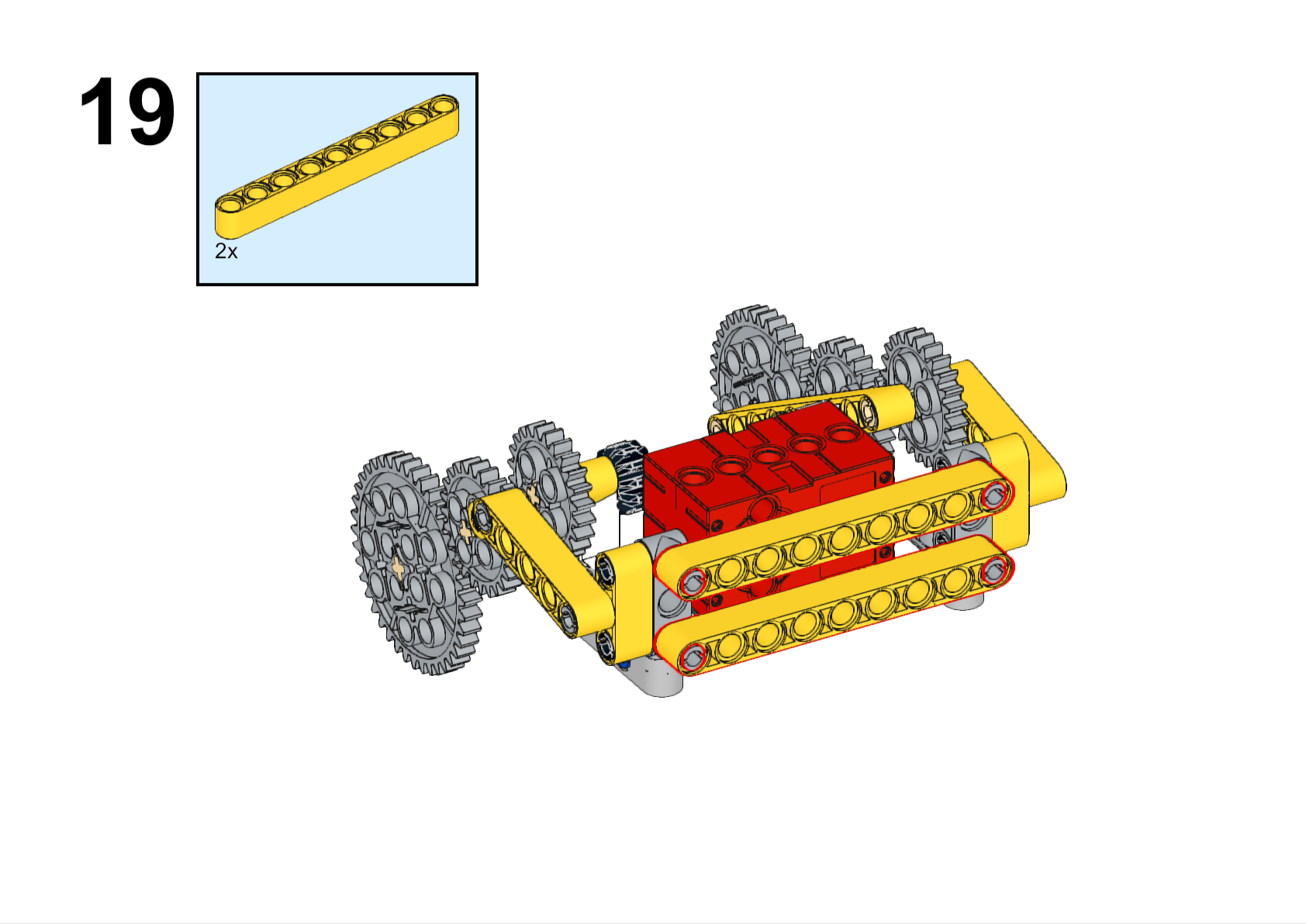
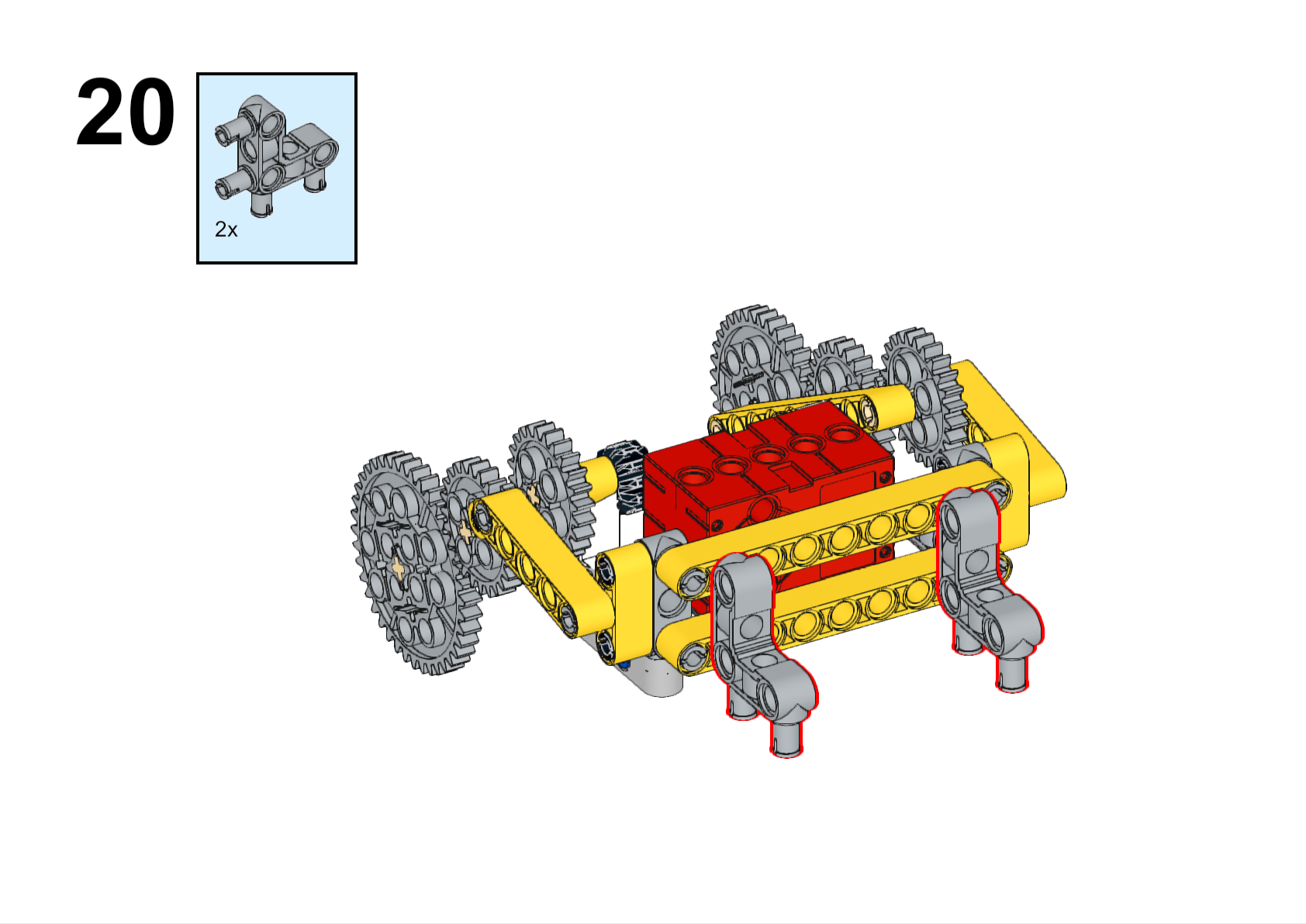
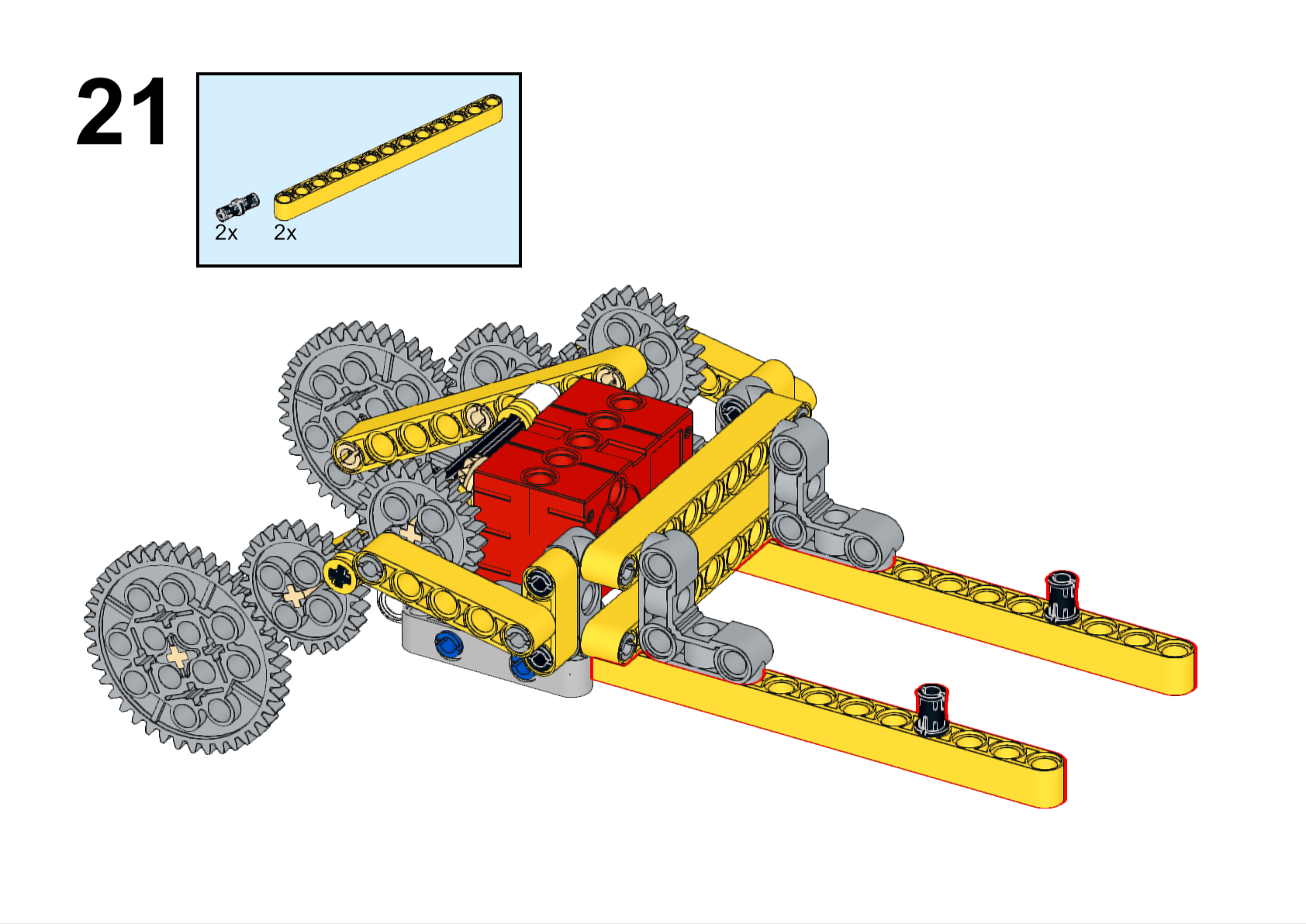
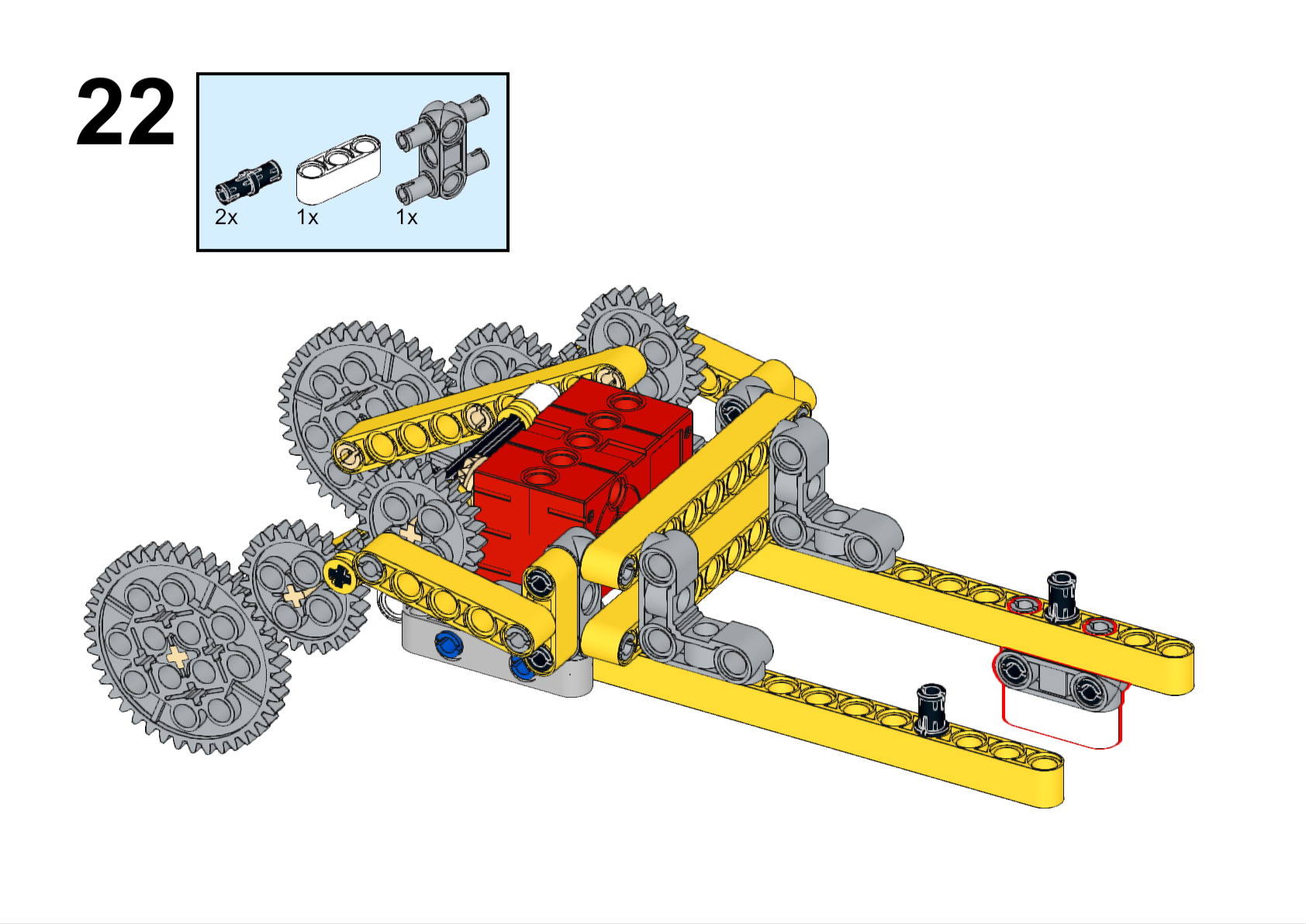
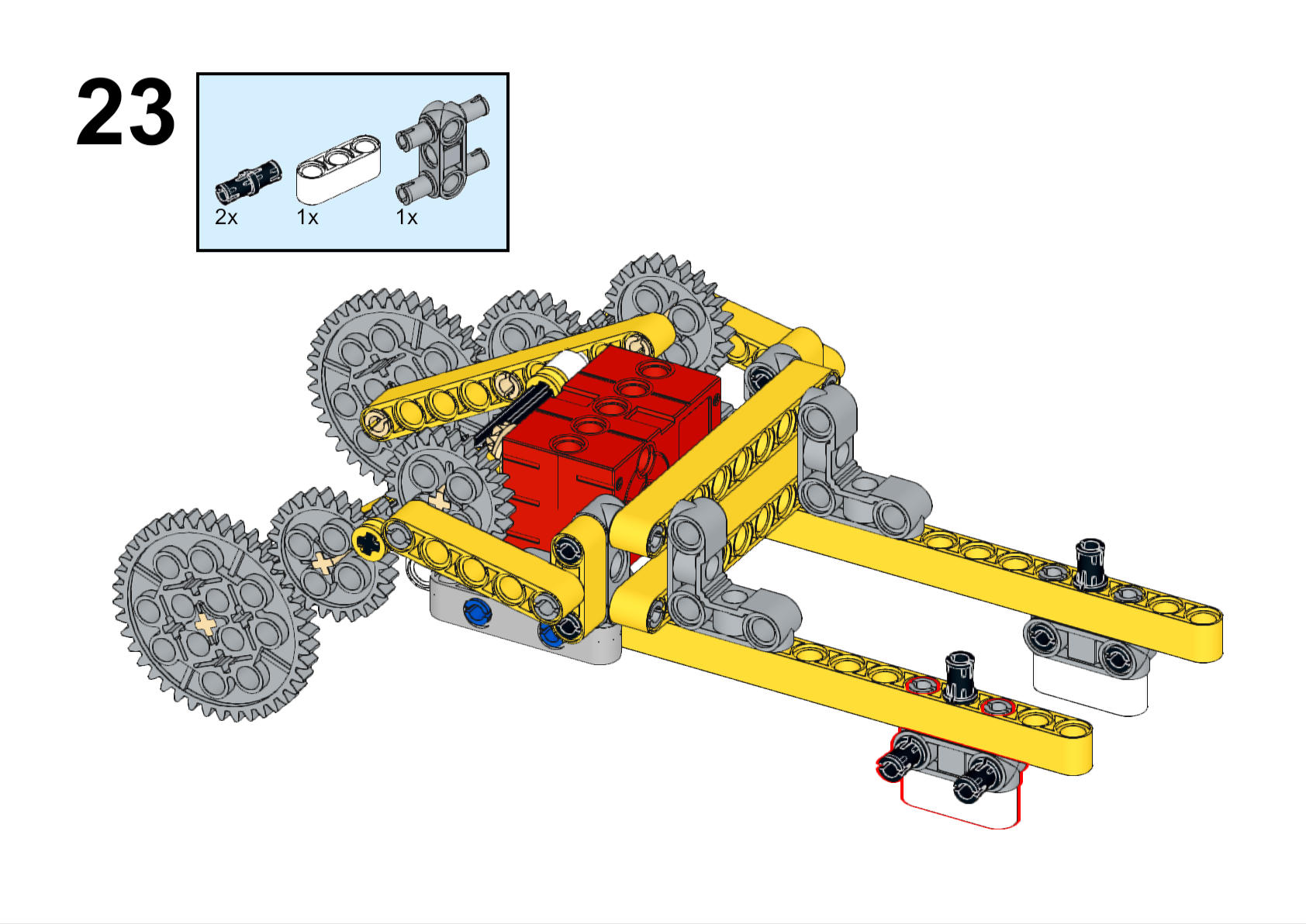
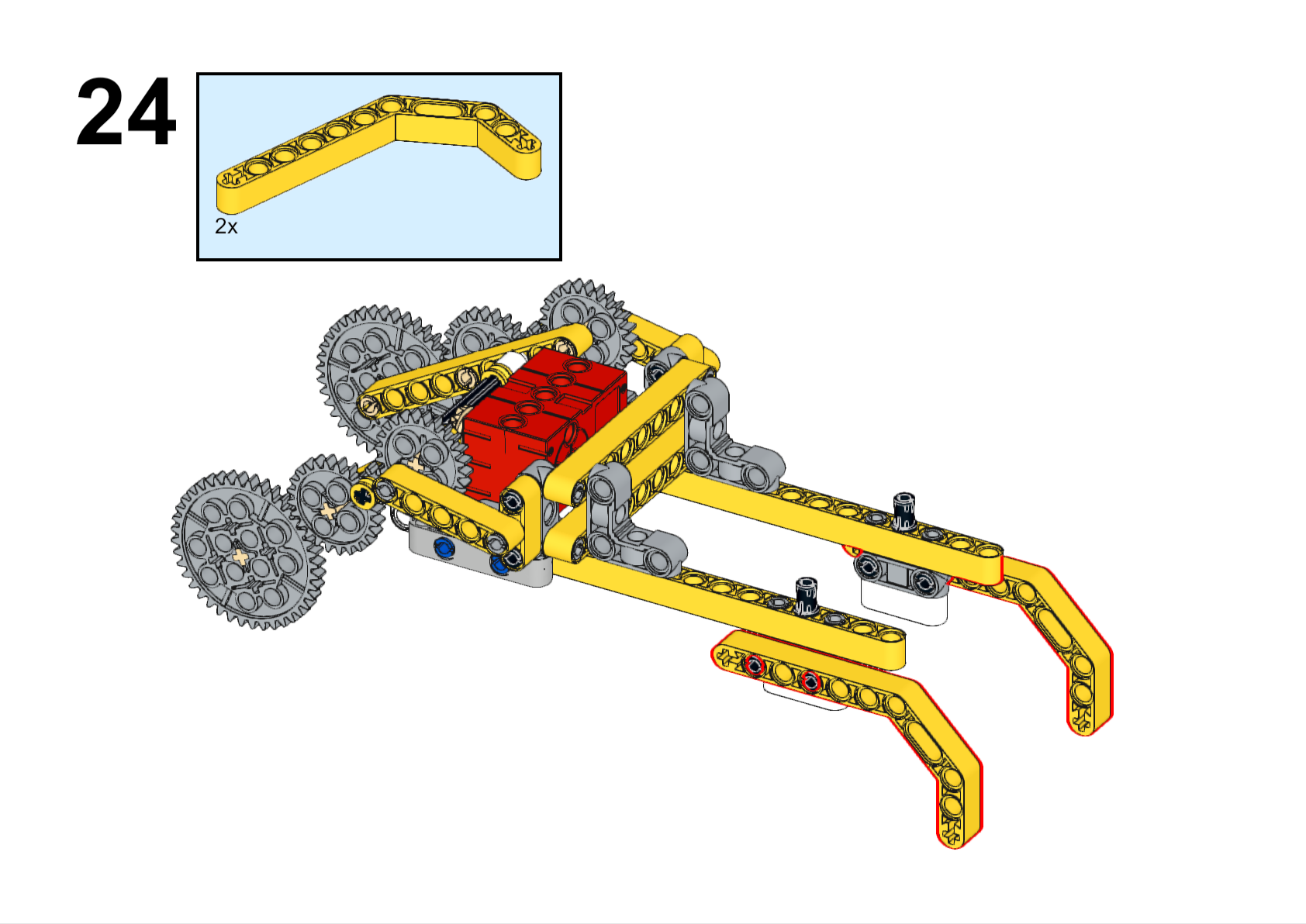
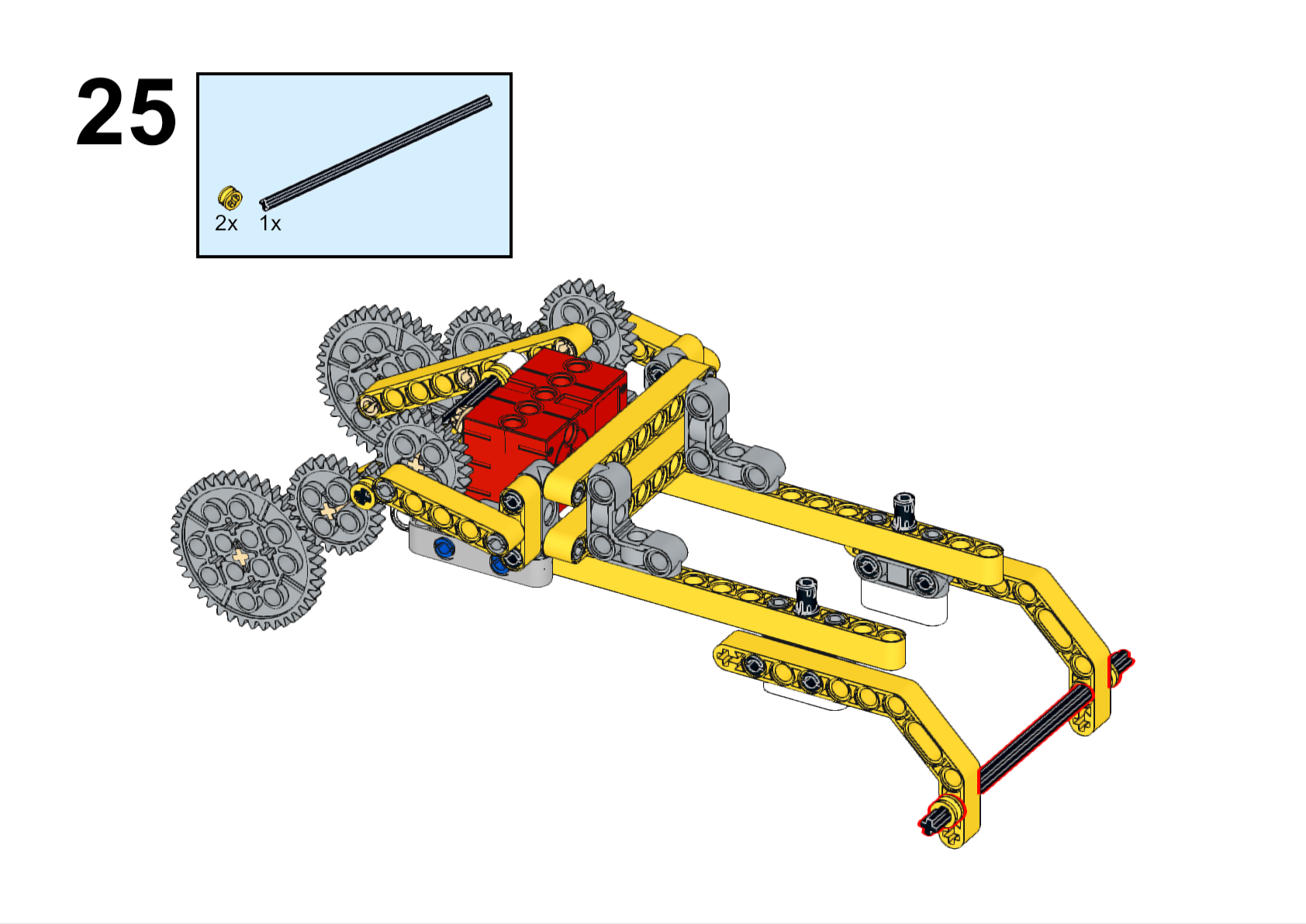
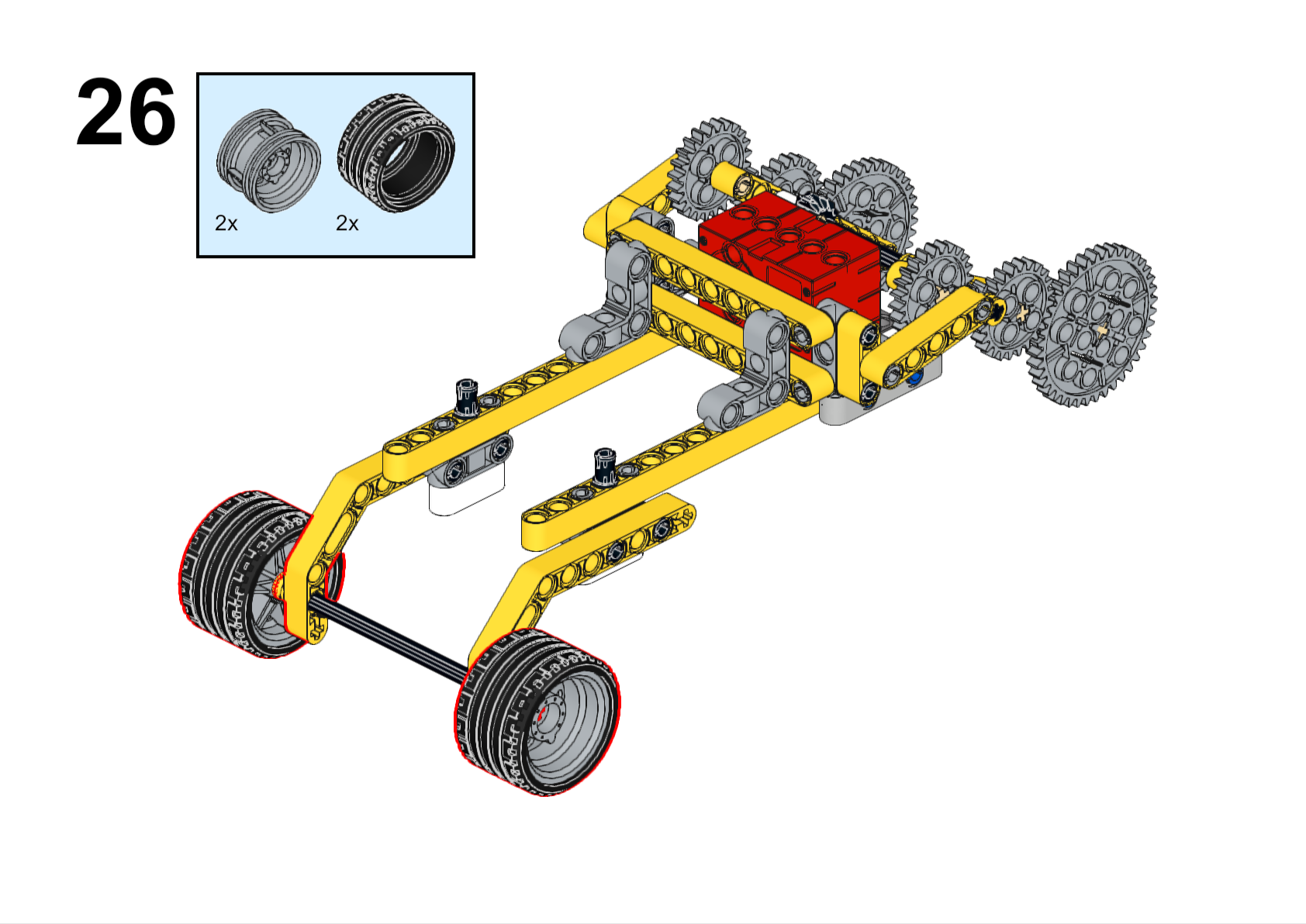
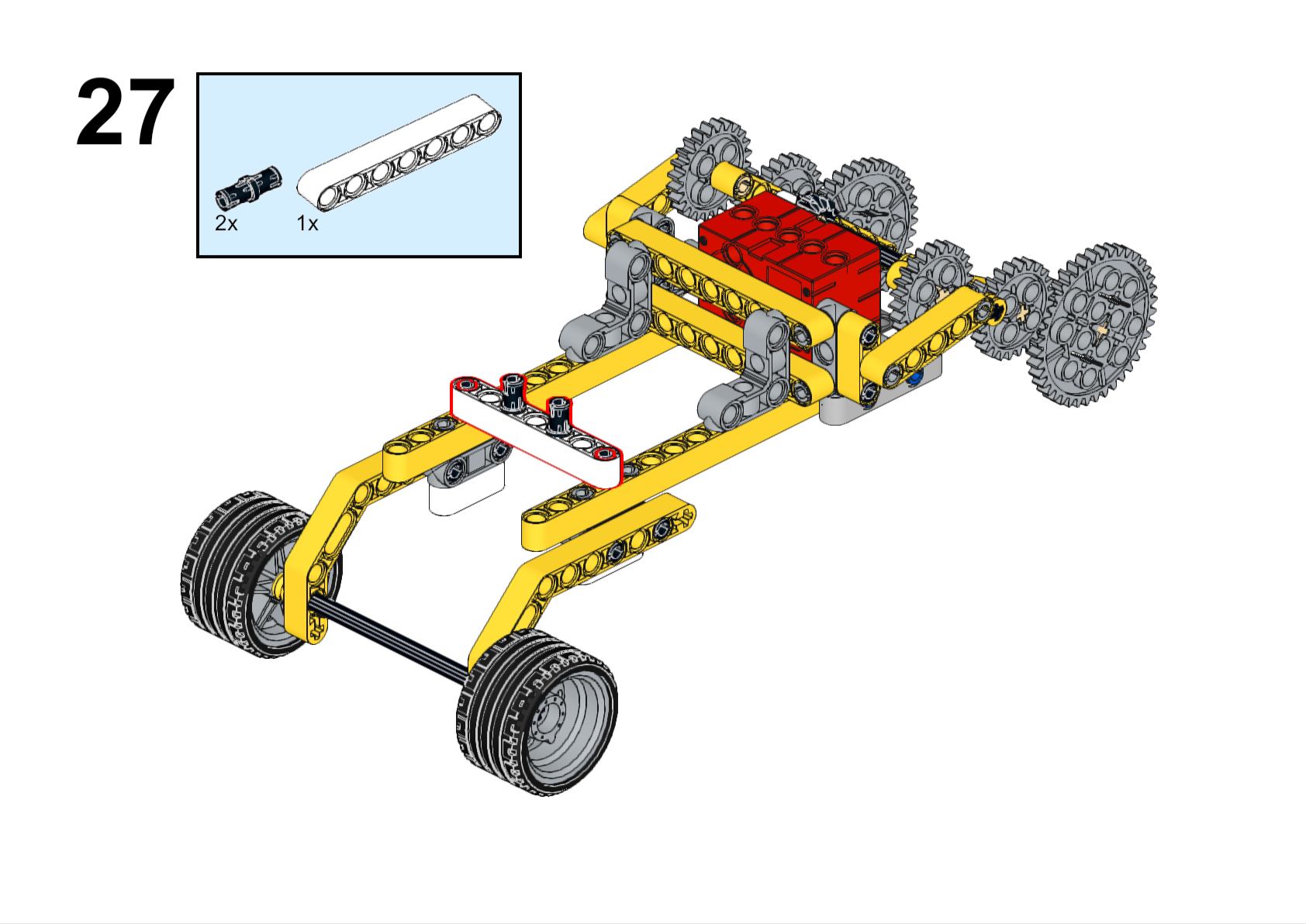
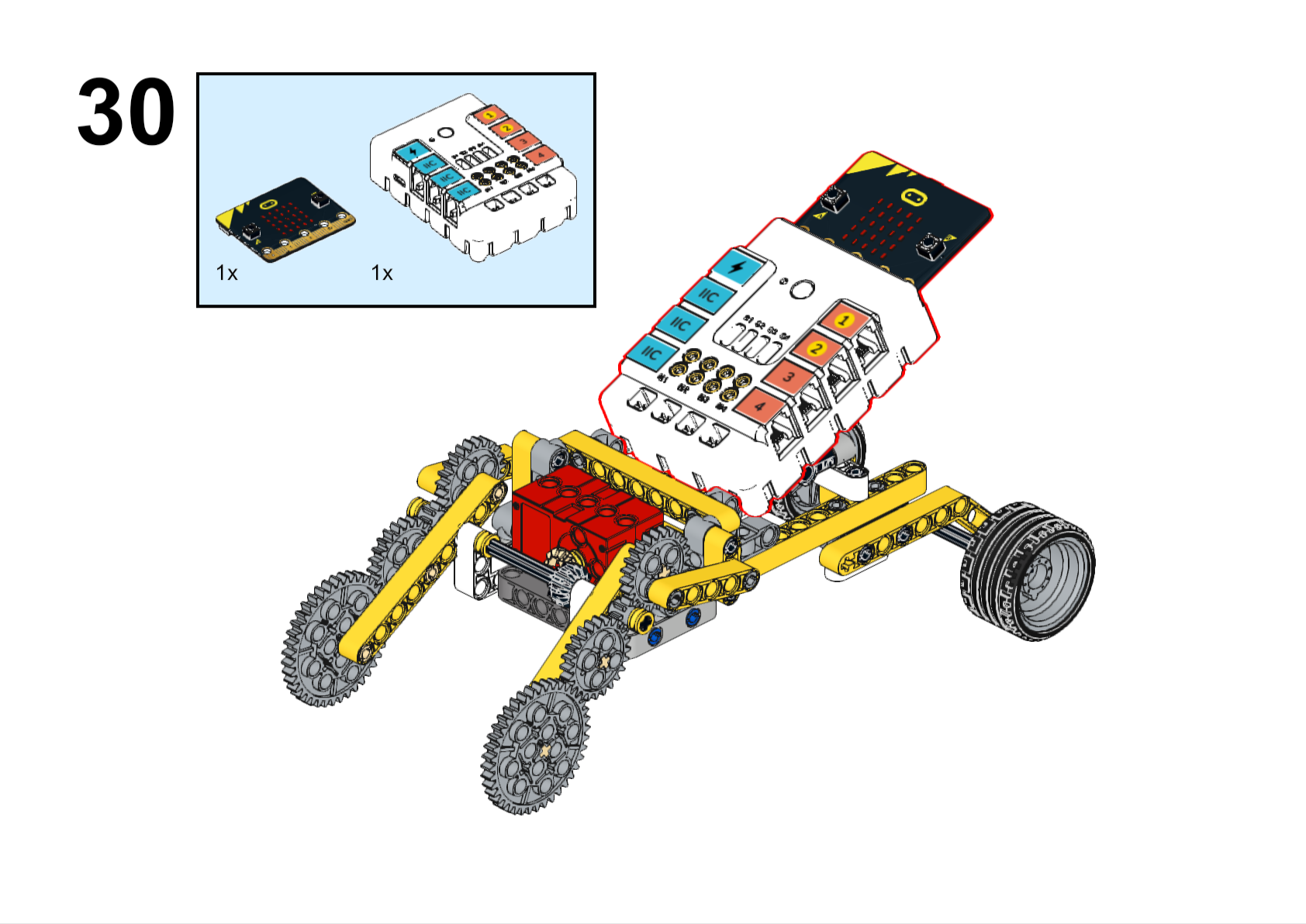
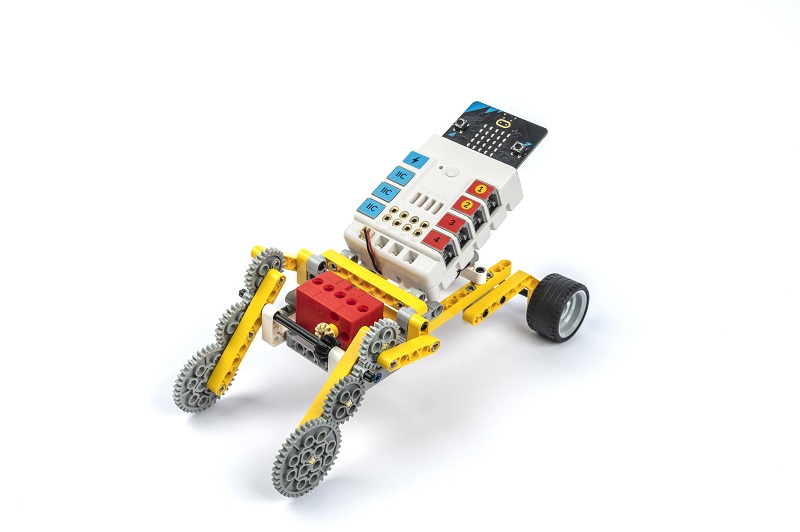
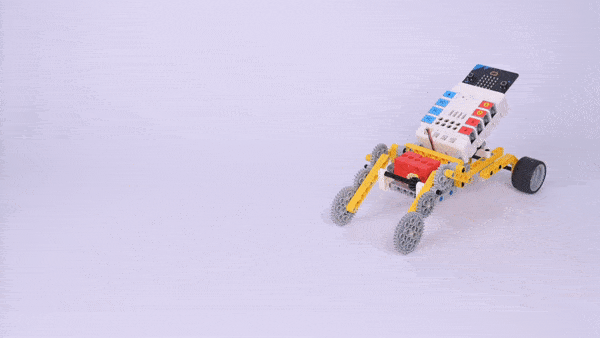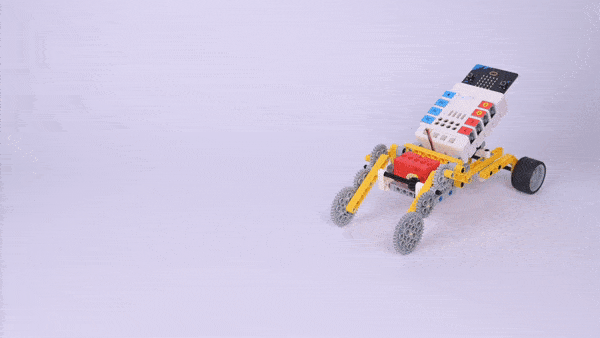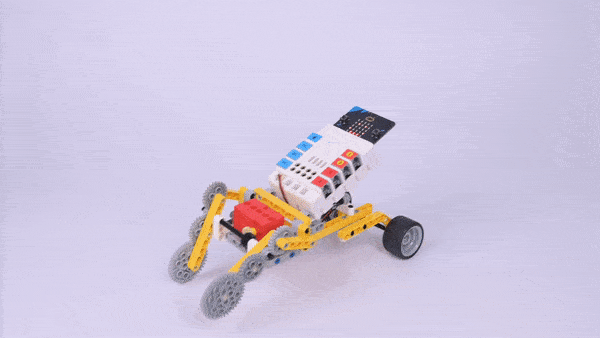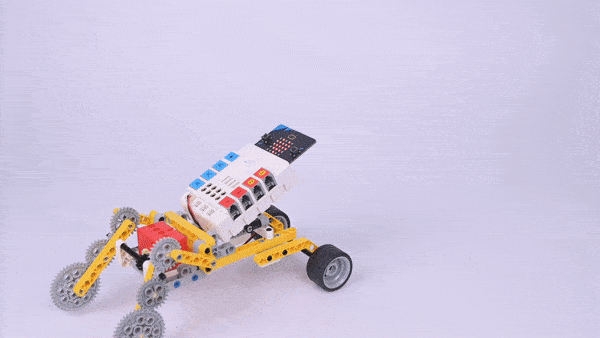
Completed

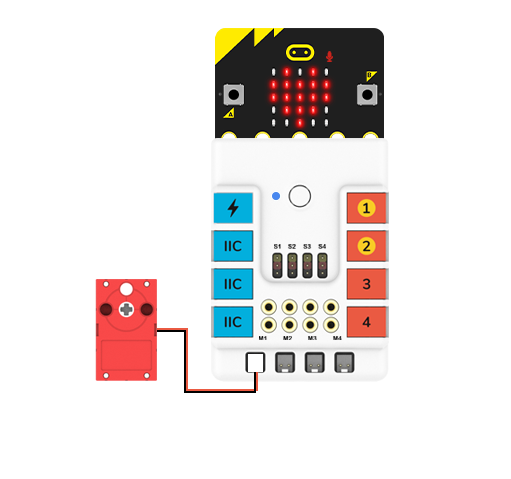
Hardware Connections
Connect the motor to the M1 port on Nezha expansion board.
Programming
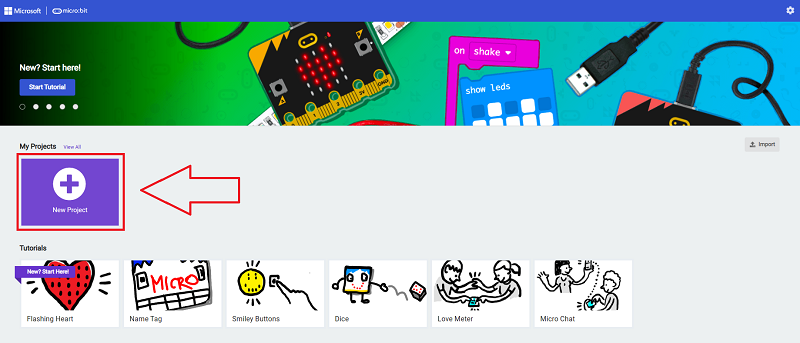
Go to makecode
Create new projects
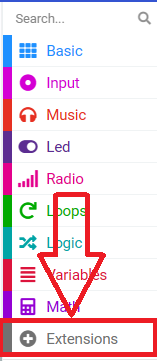
Click extensions
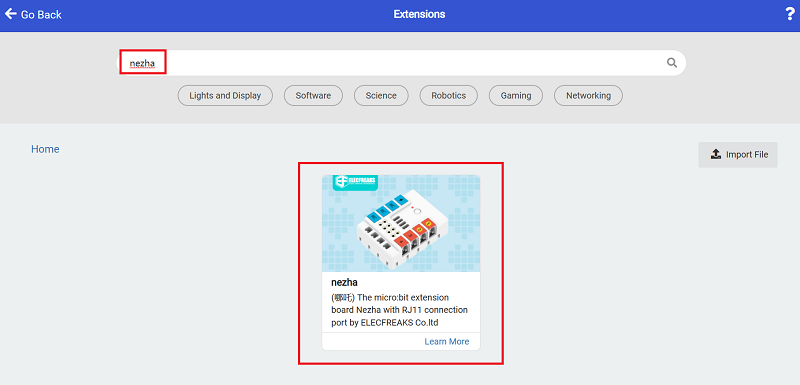
Search with nezhato add the package.
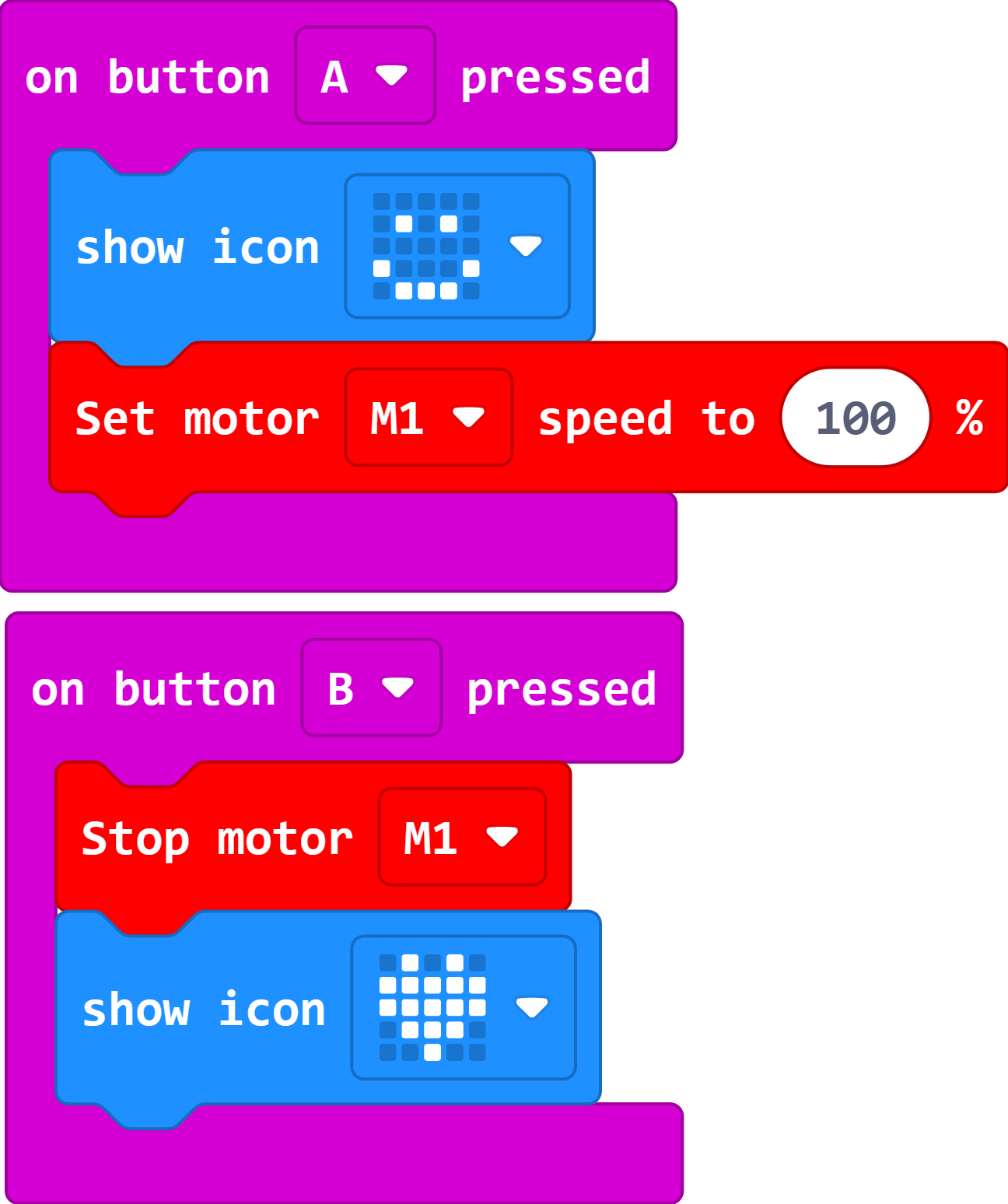
Code
Link: https://makecode.microbit.org/_i3CacvKkc40L
You may download it directly below:
Demonstration
Show in groups and have the robots in each group start crawling together and compare the results and effectiveness of each group.
Result
Press button A on the micro:bit to start the device and press button B to stop it.
Reflection
Share in groups so that students in each group can share their production process and insights, summarise the problems and solutions they encountered, and evaluate their strengths and weaknesses.