Case 02: The Growing Stormwind

Introduction
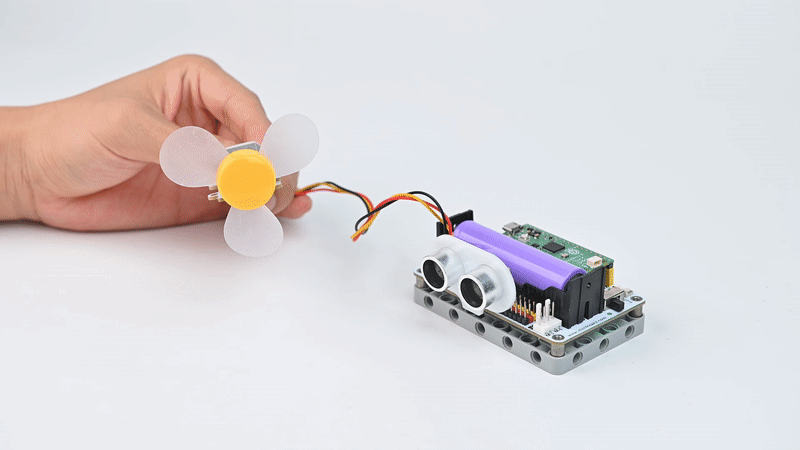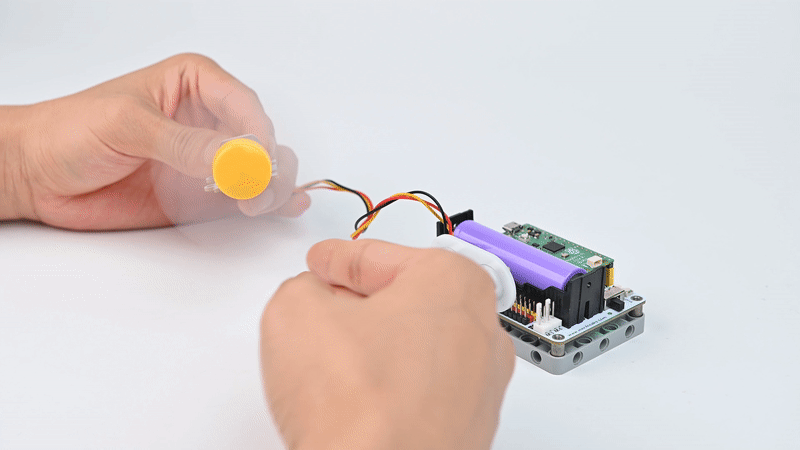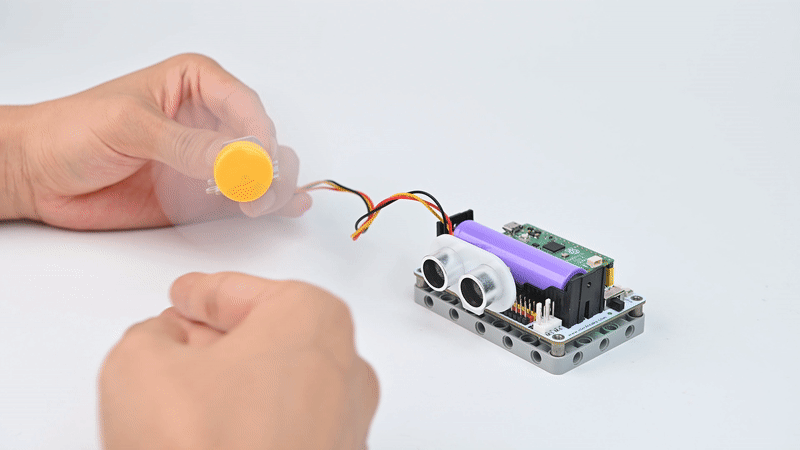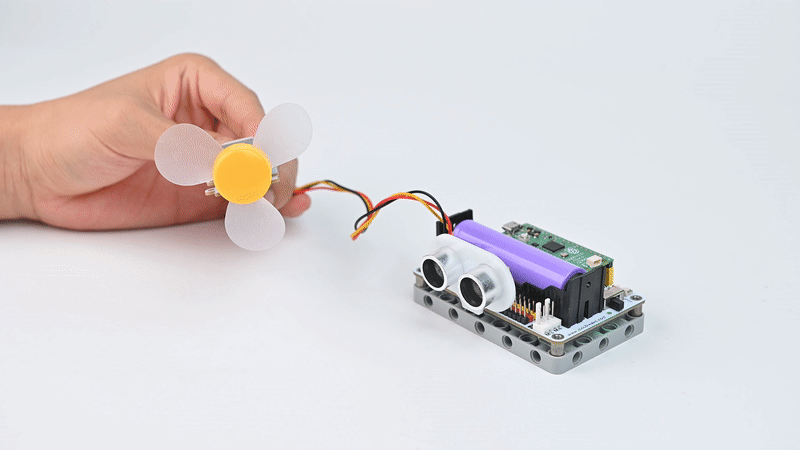
Sometimes we read in the news about tornadoes destroying houses and trees in a certain area. Although we can't experience the devastation of a tornado in real life, we can use motor fans and ultrasonic sensors to create tornadoes with variable wind speeds, and the closer we get to the ultrasonic sensors the stronger the wind.
Materials Requested
1 × Raspberry Pi Pico
1 × Wukong2040 expansion board
1 × USB cable
1 × motor fan
1 × ultrasonic sensor
1 × 3P Dupont cables with buckles
Introduction to main components
Motor
An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy into kinetic energy according to the laws of electromagnetic induction. The basic components of this motor include the armature and the stator. Armature coils are a very diverse classification of motor, in this case we are using a DC motor. When a DC voltage is applied to both ends of the motor, the motor rotates and the higher the voltage, the faster it rotates.
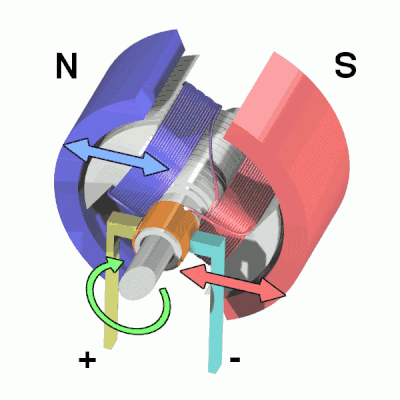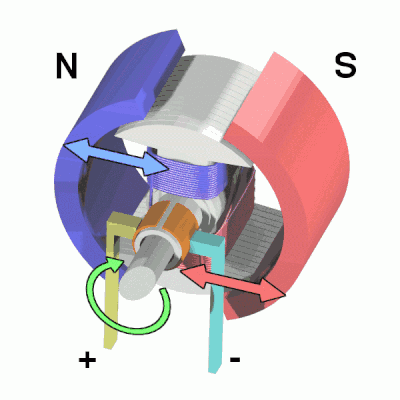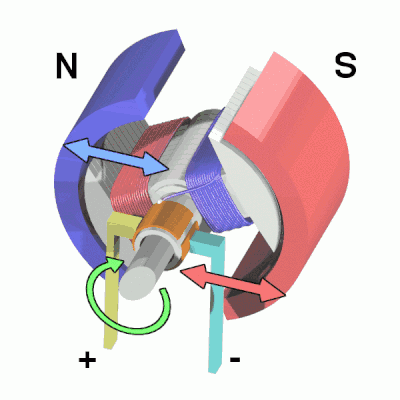
The coil is placed in a magnetic field and, through the flow of current, is repelled by the magnetic poles on one side and attracted to the poles on the other, spinning continuously under this effect. During the rotation, the current flowing in the coil is reversed so that it continues to rotate. A part of the motor called the "commutator" is powered by the "brushes", which are positioned above the "steering gear" and move continuously as it rotates. By changing the position of the brushes, the direction of the current can be changed. The commutator and brushes are essential to the rotation of the DC motor.
Ultrasonic Sensor
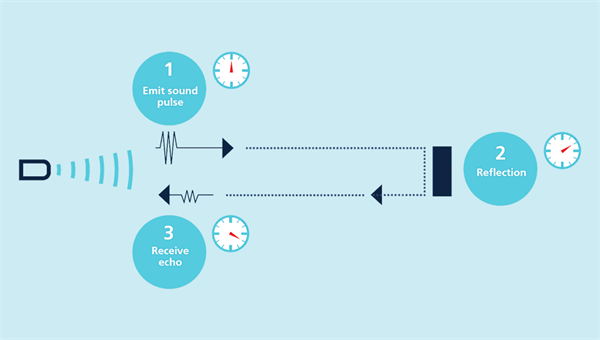
Ultrasonic sensors periodically emit short and high frequency sound waves which travel through the air at the speed of sound and if they encounter an object they will return to the sensor as an echo signal, from which the sensor can calculate the distance between the sensor and the target object by calculating the time interval between the emission of the signal and the reception of the echo.
The distance between the sensor and the object to be measured is calculated by measuring the time of flight of the sound wave, rather than by the intensity of the sound wave, and the ultrasonic sensor has a significant effect on background suppression. Almost any material that reflects sound waves, regardless of colour, can be detected by the ultrasonic sensor, including transparent materials or thin films.
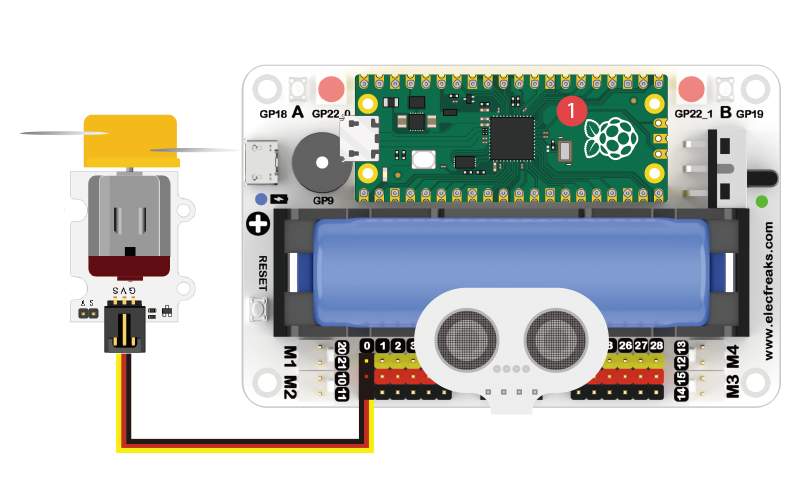
Hardware Connection
Connect your components according to the following connection diagram:
Graphical Programming
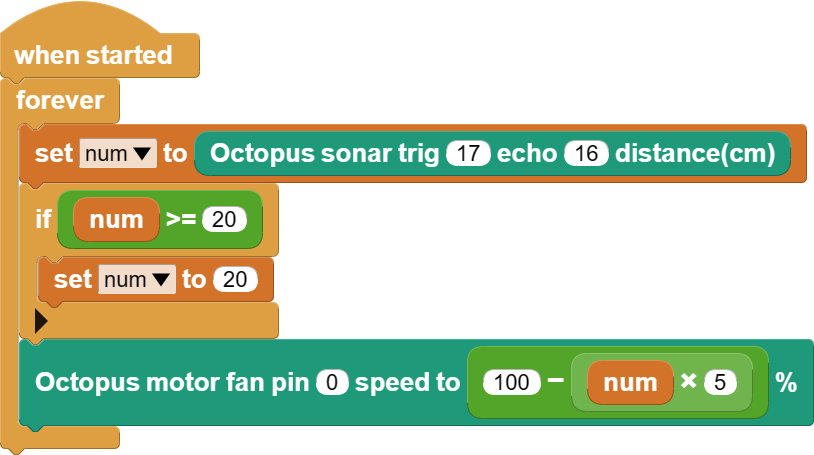
Code
from Distance import * # Import the library of the ultrasonic sensor
from Fan import * # Import the library of the motor
fan = Fan(board.GP0) # Create a motor fan object and pass in the pin number
distance = Distance(board.GP17, board.GP16) # Create the ultrasonic sensor object and pass in the pin number
while True:
num = distance.get_distance() # Get the distance value of an obstacle detected by the ultrasonic sensor and assign it to num
if num >= 20: # Determining whether an obstacle is greater than 20cm away from the ultrasound
num = 20:
fan.set_fan(100 - num * 5) # Setting the speed of the motor fan
Case Display
Think
How to make the wind weaker when we approach closer to the fan?