Case 4: Exploring the relationship between water and plant growth
Introduction
The purpose of this project is to guide students in creating an automatic watering device using the soil moisture sensor, relay module, and pump from the classroom science kit in conjunction with the micro:bit to explore the effects of water on plant growth. By monitoring soil moisture and automatically adjusting the water supply, students will learn about the importance of water to plant growth and learn basic agricultural science. This project will deepen students' understanding of physics, biology, and automation technology.

Teaching Goal
Understand the necessity of water for plant growth.
Learn how to control a water pump using soil moisture sensors and relays.
Acquire basic skills in making an automatic watering system.
Teaching Preparation
Before you begin teaching, please make sure you have the following necessary materials ready:
| Picture | Name |
|---|---|
 | classroom science kit |
 | micro:bit V2 |
 | personal computer(PC) |
 | USB cable |
These materials will provide you with a complete experience and ensure that you can follow through and learn smoothly. If you are ready for the above, we can move on to the next step.
Teaching Process
Introduction of the course
Water is the source of life and is vital for plant growth. In this lesson, we will explore the effects of water on plant growth and create an automatic watering device to keep plants hydrated for growth.
Exploratory activities
learn how to write code to read data from a soil moisture sensor using the programming environment on the micro:bit.
understand the scientific units of soil moisture and its effect on plant growth.
explore how to use a relay to control the switching on and off of a pump to automate watering.
design an experiment to record plant growth under different soil moisture conditions.
analyze the experimental data and discuss how automatic watering promotes plant growth.
Hardware Connection
Connect the soil moisture sensor to the P1 port of the wukong expansion board, the relay to the P2 port of the wukong expansion board, the water pump to the relay, and the OLED display to the IIC port of the wukong expansion board.

Code Programming
Adding Software Libraries
Clickmakecode.microbit.org, and clickNew Project.

ClickExtensions.

Searchiot-environment-kit,Add the iot-environment-kit repository.

Search for wukong and add the Wukong software library.

sample code
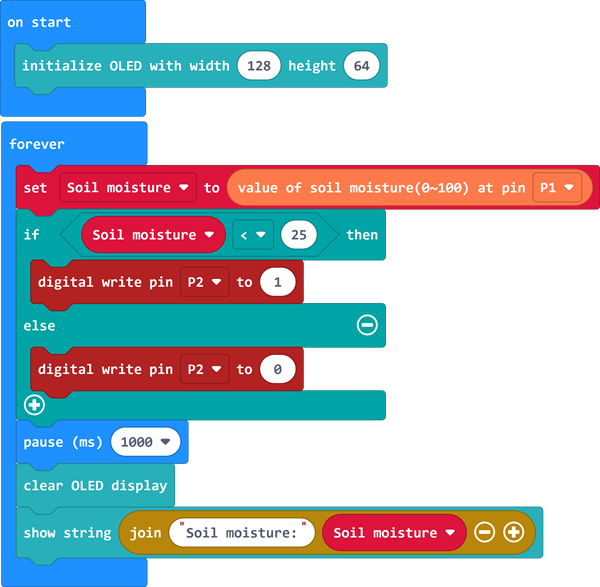
- Initializes the OLED display when the power is turned on.

- Stores the return value of the soil moisture sensor connected to port P1 into the variable Soil moisture.

- When the value of the variable Soil moisture is less than 25, set the relay connected to the P2 port to turn on the pump, otherwise set the relay connected to the P2 port to turn off the pump;

- Pause for 1000ms to clear the OLED display display and show the current soil moisture on the OLED display.
Please refer to the program link:https://makecode.microbit.org/_b2vP7K5W6KRd
You can also download the program directly from the following page.
*** Download the program ***Use the USB cable to connect the PC to the micro:bit V2.
After a successful connection, a disk drive named MICROBIT is recognized on the computer.
Click ,choose
,chooseConnect Device。
click 。
。

click 。
。
Select BBC micro:bit CMSIS-DAP in the pop-up window and then select Connect, and at this point, our micro:bit has connected successfully.

Click to download the program.
Teamwork & Presentation
Students are divided into small groups and work together to create and program cases.
Students are encouraged to cooperate, communicate and share their experiences with each other.
Each group will have the opportunity to show the cases they made and demonstrate to other groups.
Expected results: the OLED display shows the current soil moisture after powering on, and if the soil moisture is too low, the pump is automatically turned on to water.
(GIF动图)
Summary and Reflection
Review the course content and remind students what knowledge and skills they have acquired.
Lead students in a discussion about the problems and difficulties they encountered during the production process and how they solved these problems.
Guide students to think about the importance of water for plant growth and how technology can be used to optimize the environment for plant growth.
Expanding Knowledge
Water is vital to plant growth, and it plays several important roles throughout a plant's life cycle.
Nutrient Transportation: water helps plants absorb nutrients from the soil and transport those nutrients to various parts of the plant, such as leaves and fruits.
Photosynthesis: In photosynthesis, plants use water and sunlight to make the sugar and oxygen they need. Without water, this process cannot take place.
Structural Support: water also helps plants maintain their structure, allowing their stems and leaves to stay stiff.
Temperature regulation: Plants regulate their temperature by releasing water vapor through stomata on their leaves, which acts as a “sweat” for the plant and helps them stay cool in hot weather.
Effects of Too Much and Not Enough: Too much or too little water is not good for plant growth. Too much water can lead to root rot, while too little water can dry out plants and affect their growth and health.
Environmental Protection: By absorbing and storing water, plants help maintain ecological balance and environmental protection, such as reducing flooding and providing habitat.